Nfkb2 deficiency and its impact on plasma cells and immunoglobulin expression in murine small intestinal mucosa
- PMID: 35916405
- PMCID: PMC9485003
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00037.2022
Nfkb2 deficiency and its impact on plasma cells and immunoglobulin expression in murine small intestinal mucosa
Abstract
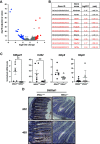
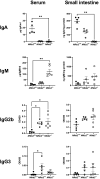
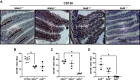
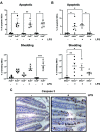
The alternative (noncanonical) nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway predominantly regulates the function of the p52/RelB heterodimer. Germline Nfkb2 deficiency in mice leads to loss of p100/p52 protein and offers protection against a variety of gastrointestinal conditions, including azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis-associated cancer and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced small intestinal epithelial apoptosis. However, the common underlying protective mechanisms have not yet been fully elucidated. We applied high-throughput RNA-Seq and proteomic analyses to characterize the transcriptional and protein signatures of the small intestinal mucosa of naïve adult Nfkb2-/- mice. Those data were validated by immunohistochemistry and quantitative ELISA using both small intestinal tissue lysates and serum. We identified a B-lymphocyte defect as a major transcriptional signature in the small intestinal mucosa and immunoglobulin A as the most downregulated protein by proteomic analysis in Nfkb2-/- mice. Small intestinal immunoglobulins were dramatically dysregulated, with undetectable levels of immunoglobulin A and greatly increased amounts of immunoglobulin M being detected. The numbers of IgA-producing, cluster of differentiation (CD)138-positive plasma cells were also reduced in the lamina propria of the small intestinal villi of Nfkb2-/- mice. This phenotype was even more striking in the small intestinal mucosa of RelB-/- mice, although these mice were equally sensitive to LPS-induced intestinal apoptosis as their RelB+/+ wild-type counterparts. NF-κB2/p52 deficiency confers resistance to LPS-induced small intestinal apoptosis and also appears to regulate the plasma cell population and immunoglobulin levels within the gut.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Novel transcriptomic analysis of murine proximal intestinal mucosa revealed an unexpected B cell signature in Nfkb2-/- mice. In-depth analysis revealed a defect in the CD38+ B cell population and a gut-specific dysregulation of immunoglobulin levels.
Keywords: NF-κB; Nfkb2; RelB; immunoglobulins; intestinal mucosa; plasma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
D.M.P. has received consultancy funding from Ipsen, Advanced Accelerator Applications and Mayoly Spindler laboratories and research funding from Trio Medicines, Ltd. None of the other authors has any conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, to disclose.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

