Virome of Giant Panda-Infesting Ticks Reveals Novel Bunyaviruses and Other Viruses That Are Genetically Close to Those from Giant Pandas
- PMID: 35916407
- PMCID: PMC9430136
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02034-22
Virome of Giant Panda-Infesting Ticks Reveals Novel Bunyaviruses and Other Viruses That Are Genetically Close to Those from Giant Pandas
Abstract
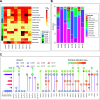
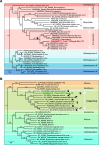
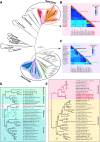
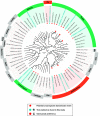
Tick infestations have been reported as one of the factors threatening the health of giant pandas, but studies of viral pathogens carried by ticks feeding on the blood of giant pandas are limited. To assess whether blood-sucking ticks of giant pandas can carry viral pathogens and if so, whether the viruses in ticks are associated with those previously detected in giant panda hosts, we determined the viromes of ticks detached from giant pandas in a field stocking area in Sichuan Province, southwest China. Using viral metagenomics we identified 32 viral species in ticks, half of which (including anellovirus [n = 9], circovirus [n = 3], and gemycircularvirus [n = 4]) showed homology to viruses carried by giant pandas and their associated host species (such as red pandas and mosquitoes) in the same living domain. Remarkably, several viruses in this study phylogenetically assigned as bunyavirus, hepe-like virus, and circovirus were detected with relatively high abundance, but whether these newly identified tick-associated viruses can replicate in ticks and then transmit to host animals during a blood meal will require further investigation. These findings further expand our understanding of the role of giant panda-infesting ticks in the local ecosystem, especially related to viral acquisition and transmission, and lay a foundation to assess the risk for giant panda exposure to tick-borne viruses. IMPORTANCE Ticks rank only second to mosquitoes as blood-feeding arthropods, capable of spreading pathogens (including viruses, bacteria, and parasites) to hosts during a blood meal. To better understand the relationship between viruses carried by ticks and viruses that have been reported in giant pandas, it is necessary to analyze the viromes of giant panda-parasitic blood-sucking ticks. This study collected 421 ticks on the body surface of giant pandas in Sichuan Province, China. We characterized the extensive genetic diversity of viruses harbored by these ticks and reported frequent communication of viruses between giant pandas and their ticks. While most of the virome discovered here are nonpathogenic viruses from giant pandas and potentially tick-specific viruses, we revealed some possible tick-borne viruses, represented by novel bunyaviruses. This research contributes to the literature because currently there are few studies on the virome of giant panda-infesting ticks.
Keywords: cross-species transmission; giant pandas; phylogenetic analysis; tick-borne viruses; ticks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The bacterial diversity and potential pathogenic risks of giant panda-infesting ticks.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0219724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02197-24. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40494644 Free PMC article.
-
Viral metagenomics unveiled extensive communications of viruses within giant pandas and their associated organisms in the same ecosystem.Sci Total Environ. 2022 May 10;820:153317. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153317. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35066043
-
Virome comparisons in wild-diseased and healthy captive giant pandas.Microbiome. 2017 Aug 7;5(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s40168-017-0308-0. Microbiome. 2017. PMID: 28780905 Free PMC article.
-
The Ecology of New Constituents of the Tick Virome and Their Relevance to Public Health.Viruses. 2019 Jun 7;11(6):529. doi: 10.3390/v11060529. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31181599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on parasites of wild and captive giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca): Diversity, disease and conservation impact.Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2020 Jul 28;13:38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2020.07.007. eCollection 2020 Dec. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2020. PMID: 32793415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The bacterial diversity and potential pathogenic risks of giant panda-infesting ticks.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0219724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02197-24. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40494644 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Mitogenomes of Ticks Ixodes acutitarsus and Ixodes ovatus Parasitizing Giant Panda: Deep Insights into the Comparative Mitogenomic and Phylogenetic Relationship of Ixodidae Species.Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 6;13(11):2049. doi: 10.3390/genes13112049. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360286 Free PMC article.
-
First Insights into the Occurrence of Circular Single-Stranded DNA Genomes in Asian and African Cattle.Animals (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;13(9):1492. doi: 10.3390/ani13091492. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37174530 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Anelloviruses Identified in Leporids from Arizona (USA).Viruses. 2025 Feb 18;17(2):280. doi: 10.3390/v17020280. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40007035 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of Viruses in Ixodes ricinus in Europe including Novel and Potential Arboviruses.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2023 Nov 21;2023:6661723. doi: 10.1155/2023/6661723. eCollection 2023. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2023. PMID: 40303763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fang L-Q, Liu K, Li X-L, Liang S, Yang Y, Yao H-W, Sun R-X, Sun Y, Chen W-J, Zuo S-Q, Ma M-J, Li H, Jiang J-F, Liu W, Yang XF, Gray GC, Krause PJ, Cao W-C. 2015. Emerging tick-borne infections in mainland China: an increasing public health threat. Lancet Infect Dis 15:1467–1479. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00177-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jia N, Wang J, Shi W, Du L, Sun Y, Zhan W, Jiang JF, Wang Q, Zhang B, Ji P, Bell-Sakyi L, Cui XM, Yuan TT, Jiang BG, Yang WF, Lam TT, Chang QC, Ding SJ, Wang XJ, Zhu JG, Ruan XD, Zhao L, Wei JT, Ye RZ, Que TC, Du CH, Zhou YH, Cheng JX, Dai PF, Guo WB, Han XH, Huang EJ, Li LF, Wei W, Gao YC, Liu JZ, Shao HZ, Wang X, Wang CC, Yang TC, Huo QB, Li W, Chen HY, Chen SE, Zhou LG, Ni XB, Tian JH, Sheng Y, Liu T, Pan YS, Tick Genome and Microbiome Consortium (TIGMIC), et al. . 2020. Large-scale comparative analyses of tick genomes elucidate their genetic diversity and vector capacities. Cell 182:1328–1340 e13. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

