Quantitative Phase Imaging: Recent Advances and Expanding Potential in Biomedicine
- PMID: 35916417
- PMCID: PMC10112851
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.1c11507
Quantitative Phase Imaging: Recent Advances and Expanding Potential in Biomedicine
Abstract
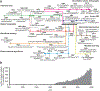
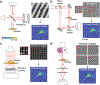
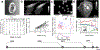
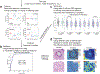
Quantitative phase imaging (QPI) is a label-free, wide-field microscopy approach with significant opportunities for biomedical applications. QPI uses the natural phase shift of light as it passes through a transparent object, such as a mammalian cell, to quantify biomass distribution and spatial and temporal changes in biomass. Reported in cell studies more than 60 years ago, ongoing advances in QPI hardware and software are leading to numerous applications in biology, with a dramatic expansion in utility over the past two decades. Today, investigations of cell size, morphology, behavior, cellular viscoelasticity, drug efficacy, biomass accumulation and turnover, and transport mechanics are supporting studies of development, physiology, neural activity, cancer, and additional physiological processes and diseases. Here, we review the field of QPI in biology starting with underlying principles, followed by a discussion of technical approaches currently available or being developed, and end with an examination of the breadth of applications in use or under development. We comment on strengths and shortcomings for the deployment of QPI in key biomedical contexts and conclude with emerging challenges and opportunities based on combining QPI with other methodologies that expand the scope and utility of QPI even further.
Keywords: biophysics; diagnostics; holography; interferometry; microscopy; phase retrieval; quantitative phase imaging; tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

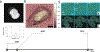
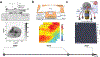
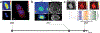
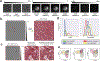
References
-
- Barer R; Joseph S Refractometry of Living Cells. Q. J. Microsc. Sci 1954, s3–95 (32), 399.
-
- Barer R; Tkaczyk S Refractive Index of Concentrated Protein Solutions. Nature 1954, 173 (4409), 821–822. - PubMed
-
- Barer R Determination of Dry Mass, Thickness, Solid and Water Concentration in Living Cells. Nature 1953, 172 (4389), 1097–1098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

