Structural and functional characterisation of a stable, broad-specificity multimeric sialidase from the oral pathogen Tannerella forsythia
- PMID: 35916484
- PMCID: PMC9472817
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20220244
Structural and functional characterisation of a stable, broad-specificity multimeric sialidase from the oral pathogen Tannerella forsythia
Abstract
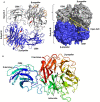
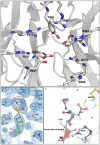
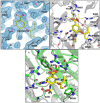
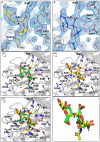
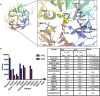
Sialidases are glycosyl hydrolase enzymes targeting the glycosidic bond between terminal sialic acids and underlying sugars. The NanH sialidase of Tannerella forsythia, one of the bacteria associated with severe periodontal disease plays a role in virulence. Here, we show that this broad-specificity enzyme (but higher affinity for α2,3 over α2,6 linked sialic acids) digests complex glycans but not those containing Neu5,9Ac. Furthermore, we show it to be a highly stable dimeric enzyme and present a thorough structural analysis of the native enzyme in its apo-form and in complex with a sialic acid analogue/ inhibitor (Oseltamivir). We also use non-catalytic (D237A) variant to characterise molecular interactions while in complex with the natural substrates 3- and 6-siallylactose. This dataset also reveals the NanH carbohydrate-binding module (CBM, CAZy CBM 93) has a novel fold made of antiparallel beta-strands. The catalytic domain structure contains novel features that include a non-prolyl cis-peptide and an uncommon arginine sidechain rotamer (R306) proximal to the active site. Via a mutagenesis programme, we identified key active site residues (D237, R212 and Y518) and probed the effects of mutation of residues in proximity to the glycosidic linkage within 2,3 and 2,6-linked substrates. These data revealed that mutagenesis of R306 and residues S235 and V236 adjacent to the acid-base catalyst D237 influence the linkage specificity preference of this bacterial sialidase, opening up possibilities for enzyme engineering for glycotechology applications and providing key structural information that for in silico design of specific inhibitors of this enzyme for the treatment of periodontitis.
Keywords: enzyme; periodontitis; sialic acid; sialidase.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Li, C., Yang, X., Pan, Y., Yu, N., Xu, X., Tong, T.et al. (2017) A sialidase-deficient Porphyromonas gingivalis mutant strain induces less interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in Epi4 cells than W83 strain through regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. J. Periodontol. 88, e129–e139 10.1902/jop.2017.160815 - DOI - PubMed

