A Bispecific Antibody Targeting RBD and S2 Potently Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Other Variants of Concern
- PMID: 35916510
- PMCID: PMC9400488
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00775-22
A Bispecific Antibody Targeting RBD and S2 Potently Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Other Variants of Concern
Abstract
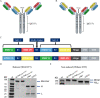
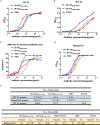
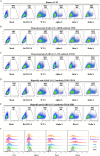
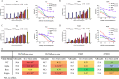
Emerging severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants, especially the Omicron variant, have impaired the efficacy of existing vaccines and most therapeutic antibodies, highlighting the need for additional antibody-based tools that can efficiently neutralize emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. The use of a "single" agent to simultaneously target multiple distinct epitopes on the spike is desirable in overcoming the neutralizing escape of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Herein, we generated a human-derived IgG-like bispecific antibody (bsAb), Bi-Nab35B5-47D10, which successfully retained parental specificity and simultaneously bound to the two distinct epitopes on receptor-binding domain (RBD) and S2. Bi-Nab35B5-47D10 showed improved spike binding breadth among wild-type (WT) SARS-CoV-2, variants of concern (VOCs), and variants being monitored (VBMs) compared with its parental monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). Furthermore, pseudotyped virus neutralization demonstrated that Bi-Nab35B5-47D10 can efficiently neutralize VBMs, including Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), and Kappa (B.1.617.1), as well as VOCs, including Delta (B.1.617.2), Omicron BA.1, and Omicron BA.2. Crucially, Bi-Nab35B5-47D10 substantially improved neutralizing activity against Omicron BA.1 (IC50 = 0.15 nM) and Omicron BA.2 (IC50 = 0.67 nM) compared with its parental MAbs. Therefore, Bi-Nab35B5-47D10 represents a potential effective countermeasure against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and other variants of concern. IMPORTANCE The new, highly contagious SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant caused substantial breakthrough infections and has become the dominant strain in countries across the world. Omicron variants usually bear high mutations in the spike protein and exhibit considerable escape of most potent neutralization monoclonal antibodies and reduced efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines. The development of neutralizing antibodies with potent efficacy against the Omicron variant is still an urgent priority. Here, we generated a bsAb, Bi-Nab35B5-47D10, which simultaneously targets SARS-CoV-2 RBD and S2 and improves the neutralizing potency and breadth against SARS-CoV-2 WT and the tested variants compared with their parental antibodies. Notably, Bi-Nab35B5-47D10 has more potent neutralizing activity against the VOC Omicron pseudotyped virus. Therefore, Bi-Nab35B5-47D10 is a feasible and potentially effective strategy by which to treat and prevent COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Omicron variants; SARS-CoV-2; bispecific antibodies; neutralization; neutralizing antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Emerging Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Novel Therapeutics Against Coronavirus (COVID-19).2023 May 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 May 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 34033342 Free Books & Documents.
-
An RBD bispecific antibody effectively neutralizes a SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant.One Health Adv. 2023;1(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s44280-023-00012-0. Epub 2023 Apr 30. One Health Adv. 2023. PMID: 37521533 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into hybridoma-derived neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against Omicron BA.5 and XBB.1.16 variants of SARS-CoV-2.J Virol. 2025 Feb 25;99(2):e0130724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01307-24. Epub 2025 Jan 7. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 39772622 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variants to Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0092622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00926-22. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35700134 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Functions and Clinical Significance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Corcern.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 20;9:849217. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.849217. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35669924 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Status and Developing Strategies for Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Therapy in the Omicron Era of COVID-19.Viruses. 2023 May 31;15(6):1297. doi: 10.3390/v15061297. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37376597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broadening sarbecovirus neutralization with bispecific antibodies combining distinct conserved targets on the receptor binding domain.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2388344. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2388344. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39165108 Free PMC article.
-
Bispecific antibodies with broad neutralization potency against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 6:2024.05.05.592584. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.05.592584. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38766244 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Evaluation of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgA Response in Tears of Vaccinated COVID-19 Subjects.Viruses. 2023 Jan 30;15(2):399. doi: 10.3390/v15020399. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851613 Free PMC article.
-
Function and mechanism of bispecific antibodies targeting SARS-CoV-2.Cell Insight. 2024 Feb 3;3(2):100150. doi: 10.1016/j.cellin.2024.100150. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cell Insight. 2024. PMID: 38374826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arora P, Kempf A, Nehlmeier I, Graichen L, Sidarovich A, Winkler MS, Schulz S, Jäck H-M, Stankov MV, Behrens GMN, Pöhlmann S, Hoffmann M. 2021. Delta variant (B.1.617.2) sublineages do not show increased neutralization resistance. Cell Mol Immunol 18:2557–2559. 10.1038/s41423-021-00772-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruel T, Hadjadj J, Maes P, Planas D, Seve A, Staropoli I, Guivel-Benhassine F, Porrot F, Bolland W-H, Nguyen Y, Casadevall M, Charre C, Péré H, Veyer D, Prot M, Baidaliuk A, Cuypers L, Planchais C, Mouquet H, Baele G, Mouthon L, Hocqueloux L, Simon-Loriere E, André E, Terrier B, Prazuck T, Schwartz O. 2022. Serum neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages BA.1 and BA.2 in patients receiving monoclonal antibodies. Nat Med 28:1297–1302. 10.1038/s41591-022-01792-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mlcochova P, Kemp SA, Dhar MS, Papa G, Meng B, Ferreira IATM, Datir R, Collier DA, Albecka A, Singh S, Pandey R, Brown J, Zhou J, Goonawardane N, Mishra S, Whittaker C, Mellan T, Marwal R, Datta M, Sengupta S, Ponnusamy K, Radhakrishnan VS, Abdullahi A, Charles O, Chattopadhyay P, Devi P, Caputo D, Peacock T, Wattal C, Goel N, Satwik A, Vaishya R, Agarwal M, Mavousian A, Lee JH, Bassi J, Silacci-Fegni C, Saliba C, Pinto D, Irie T, Yoshida I, Hamilton WL, Sato K, Bhatt S, Flaxman S, James LC, Corti D, Piccoli L, Barclay WS, Rakshit P, CITIID-NIHR BioResource COVID-19 Collaboration , et al.. 2021. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant replication and immune evasion. Nature 599:114–119. 10.1038/s41586-021-03944-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Iketani S, Guo Y, Chan JF-W, Wang M, Liu L, Luo Y, Chu H, Huang Y, Nair MS, Yu J, Chik KK-H, Yuen TT-T, Yoon C, To KK-W, Chen H, Yin MT, Sobieszczyk ME, Huang Y, Wang HH, Sheng Z, Yuen K-Y, Ho DD. 2022. Striking antibody evasion manifested by the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 602:676–681. 10.1038/s41586-021-04388-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Planas D, Veyer D, Baidaliuk A, Staropoli I, Guivel-Benhassine F, Rajah MM, Planchais C, Porrot F, Robillard N, Puech J, Prot M, Gallais F, Gantner P, Velay A, Le Guen J, Kassis-Chikhani N, Edriss D, Belec L, Seve A, Courtellemont L, Péré H, Hocqueloux L, Fafi-Kremer S, Prazuck T, Mouquet H, Bruel T, Simon-Lorière E, Rey FA, Schwartz O. 2021. Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization. Nature 596:276–280. 10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

