A Biofeedback-Based Mobile App With Serious Games for Young Adults With Anxiety in the United Arab Emirates: Development and Usability Study
- PMID: 35916692
- PMCID: PMC9382548
- DOI: 10.2196/36936
A Biofeedback-Based Mobile App With Serious Games for Young Adults With Anxiety in the United Arab Emirates: Development and Usability Study
Abstract
Background: Following the outbreak of COVID-19, several studies have reported that young adults encountered a rise in anxiety symptoms, which could negatively affect their quality of life. Promising evidence suggests that mobile apps with biofeedback, serious games, breathing exercises, and positive messaging, among other features, are useful for anxiety self-management and treatment.
Objective: This study aimed to develop and evaluate the usability of a biofeedback-based app with serious games for young adults with anxiety in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
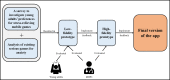
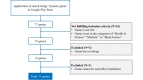
Methods: This study consists of two phases: Phase I describes the design and development of the app, while Phase II presents the results of a usability evaluation by experts. To elicit the app's requirements during Phase I, we conducted (1) a survey to investigate preferences of young adults in the UAE for mobile games for stress relief; (2) an analysis of serious games for anxiety; and (3) interviews with mental health professionals and young adults in the UAE. In Phase II, five experts tested the usability of the developed app using a set of Nielsen's usability heuristics.
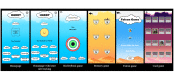
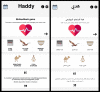
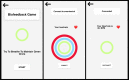
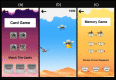
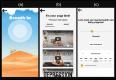
Results: A fully functional biofeedback-based app with serious games was co-designed with mental health professionals. The app included 4 games (ie, a biofeedback game, card game, arcade game, and memory game), 2 relaxation techniques (ie, a breathing exercise and yoga videos), and 2 additional features (ie, positive messaging and a mood tracking calendar). The results of Phase II showed that the developed app is efficient, simple, and easy to use. Overall, the app design scored an average of 4 out of 5.
Conclusions: The elicitation techniques used in Phase I resulted in the development of an easy-to-use app for the self-management of anxiety. Further research is required to determine the app's usability and effectiveness in the target population.
Keywords: anxiety; app; biofeedback; connected mental health; development; digital game; gamification; gaming; mHealth; mental health; mobile health; serious game; stress; stress relief; usability; user experience; user feedback; user need; user-centered design; user-centred design; young adult; youth.
©Mariam Almeqbaali, Sofia Ouhbi, Mohamed Adel Serhani, Leena Amiri, Reem K Jan, Nazar Zaki, Ayman Sharaf, Abdulla Al Helali, Eisa Almheiri. Originally published in JMIR Serious Games (https://games.jmir.org), 02.08.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Mobile Phone-Based App for Use During Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Adolescents With Anxiety (MindClimb): User-Centered Design and Usability Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Dec 8;8(12):e18439. doi: 10.2196/18439. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 33289671 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of user satisfaction and usability of a mobile app for smoking cessation.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019 Dec;182:105042. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105042. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31473444
-
Development of an Ambulatory Biofeedback App to Enhance Emotional Awareness in Patients with Borderline Personality Disorder: Multicycle Usability Testing Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Oct 15;7(10):e13479. doi: 10.2196/13479. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019. PMID: 31617851 Free PMC article.
-
Ten Steps to Design a Counseling App to Reduce the Psychosocial Impact of Human Papillomavirus Testing on the Basis of a User-Centered Design Approach in a Low- and Middle-Income Setting.JCO Glob Oncol. 2022 Oct;8:e2200168. doi: 10.1200/GO.22.00168. JCO Glob Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36252163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serious digital games for diabetes Mellitus: A scoping review of its current State, Accessibility, and functionality for patients and healthcare providers.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024 Oct;216:111833. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2024.111833. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 39179114
Cited by
-
Co-producing digital mental health interventions: A systematic review.Digit Health. 2024 Apr 25;10:20552076241239172. doi: 10.1177/20552076241239172. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38665886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smartphone-based serious games for mental health: a scoping review.Multimed Tools Appl. 2024;83(36):84047-84094. doi: 10.1007/s11042-024-18971-w. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Multimed Tools Appl. 2024. PMID: 39553422 Free PMC article.
-
Personalization variables in digital mental health interventions for depression and anxiety in adolescents and youth: a scoping review.Front Digit Health. 2025 May 15;7:1500220. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1500220. eCollection 2025. Front Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40444184 Free PMC article.
-
An Internet- and Kinect-Based Multiple Sclerosis Fitness Intervention Training With Pilates Exercises: Development and Usability Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2023 Nov 8;11:e41371. doi: 10.2196/41371. JMIR Serious Games. 2023. PMID: 37938895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheikh Ismail L, Mohamad MN, Bataineh MF, Ajab A, Al-Marzouqi AM, Jarrar AH, Abu Jamous DO, Ali HI, Al Sabbah H, Hasan H, Stojanovska L, Hashim M, Shaker Obaid RR, Saleh ST, Osaili TM, Al Dhaheri AS. Impact of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19) lockdown on mental health and well-being in the United Arab Emirates. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:633230. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.633230. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.633230. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drissi N, Alhmoudi A, Al Nuaimi H, Alkhyeli M, Alsalami S, Ouhbi S. Investigating the impact of COVID-19 lockdown on the psychological health of university students and their attitudes toward mobile mental health solutions: Two-part questionnaire study. JMIR Form Res. 2020 Oct 20;4(10):e19876. doi: 10.2196/19876. https://formative.jmir.org/2020/10/e19876/ v4i10e19876 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saddik B, Hussein A, Sharif-Askari FS, Kheder W, Temsah MH, Koutaich RA, Haddad ES, Al-Roub NM, Marhoon FA, Hamid Q, Halwani R. Increased levels of anxiety among medical and non-medical university students during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Arab Emirates. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2020;13:2395–2406. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S273333. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S273333.273333 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thomas J, Barbato M, Verlinden M, Gaspar C, Moussa M, Ghorayeb J, Menon A, Figueiras MJ, Arora T, Bentall RP. Psychosocial correlates of depression and anxiety in the United Arab Emirates during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:564172. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.564172. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.564172. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anxiety Disorders. WebMD. [2021-11-11]. https://www.webmd.com/anxiety-panic/guide/anxiety-disorders .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

