Current status of type 1 (IgG4-related) autoimmune pancreatitis
- PMID: 35916965
- PMCID: PMC9522839
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-022-01891-7
Current status of type 1 (IgG4-related) autoimmune pancreatitis
Abstract
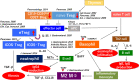
In 1995, Yoshida et al. proposed first the concept of "autoimmune pancreatitis" (AIP). Since then, AIP has been accepted as a new pancreatic inflammatory disease and is now divided two subtypes. Type 1 AIP affected immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) and implicates the pancreatic manifestation of IgG4-related disease, while type 2 is characterized by neutrophil infiltration and granulocytic epithelial lesions (GEL). Recent research has clarified the clinical and pathophysiological aspects of type 1 AIP, which is more than type 2 among the Japanese population. However, many details remain unclear about the pathogenesis and progression of this disease. In this review, we discuss the current knowledge and recent advances relating to type 1 AIP.
Keywords: Autoimmune pancreatitis; Basophil; IgG4; M2 macrophage; Regulatory T cells.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in relation to this study.
Figures
References
-
- Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratore R, et al. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas–an autonomous pancreatic disease? Am J Dig Dis. 1961;6:688–698. - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi K, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis with cholangitis: a variant of primary sclerosing cholangitis extensively involving pancreas. Hum Pathol. 1991;22:387–395. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, et al. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:1561–8. - PubMed
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Ito T, Nakano I, Koyanagi S, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis as a new clinical entity three cases of autoimmune pancreatitis with effective steroid therapy. Dig Dis Sci. 1997;42:1458–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 24591020/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 20590810/Japan Science Society
- 23591017/Japan Science Society
- 24591020/Japan Science Society
- 12008507/Japan Science Society
- 17877850/Japan Science Society
- 17K09468/Japan Science Society
- 15K09052/Japan Science Society
- 17824893/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- 15K09052/Ministry of Culture and Science of Japan
- 18K0792/Ministry of Culture and Science of Japan
- 121K07943/Ministry of Culture and Science of Japan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

