Quantum Dots Compete at the Acme of MXene Family for the Optimal Catalysis
- PMID: 35916985
- PMCID: PMC9346050
- DOI: 10.1007/s40820-022-00908-3
Quantum Dots Compete at the Acme of MXene Family for the Optimal Catalysis
Abstract
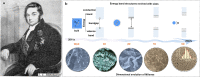
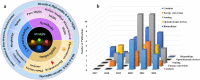
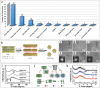
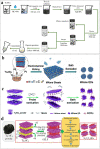
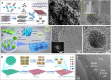
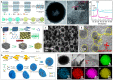
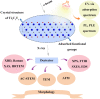
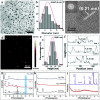
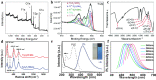
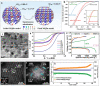
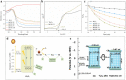
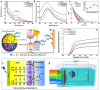
It is well known that two-dimensional (2D) MXene-derived quantum dots (MQDs) inherit the excellent physicochemical properties of the parental MXenes, as a Chinese proverb says, "Indigo blue is extracted from the indigo plant, but is bluer than the plant it comes from." Therefore, 0D QDs harvest larger surface-to-volume ratio, outstanding optical properties, and vigorous quantum confinement effect. Currently, MQDs trigger enormous research enthusiasm as an emerging star of functional materials applied to physics, chemistry, biology, energy conversion, and storage. Since the surface properties of small-sized MQDs include the type of surface functional groups, the functionalized surface directly determines their performance. As the Nobel Laureate Wolfgang Pauli says, "God made the bulk, but the surface was invented by the devil," and it is just on the basis of the abundant surface functional groups, there is lots of space to be thereof excavated from MQDs. We are witnessing such excellence and even more promising to be expected. Nowadays, MQDs have been widely applied to catalysis, whereas the related reviews are rarely reported. Herein, we provide a state-of-the-art overview of MQDs in catalysis over the past five years, ranging from the origin and development of MQDs, synthetic routes of MQDs, and functionalized MQDs to advanced characterization techniques. To explore the diversity of catalytic application and perspectives of MQDs, our review will stimulate more efforts toward the synthesis of optimal MQDs and thereof designing high-performance MQDs-based catalysts.
Keywords: Catalysis; MXene; Quantum dots; Structure; Surface groups.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures











References
-
- Winderlich R. Jons Jakob Berzelius. J. Chem. Educ. 1948;25(9):500. doi: 10.1021/ed025p500. - DOI
-
- Morachevskii AG. Jons Jakob Berzelius (to 225th anniversary of his birthday) Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2004;77:1388–1391. doi: 10.1007/s11167-005-0037-1. - DOI
-
- Rupert FF. The solid hydrates of ammonia II. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1910;32(6):748–749. doi: 10.1021/ja01924a004. - DOI
-
- Ling C, Bai X, Ouyang Y, Du A, Wang J. Single molybdenum atom anchored on N-doped carbon as a promising electrocatalyst for nitrogen reduction into ammonia at ambient conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2018;122:16842–16847. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b05257. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
