Treatment of ovarian cancer with modified anthrax toxin
- PMID: 35917343
- PMCID: PMC9371659
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2210179119
Treatment of ovarian cancer with modified anthrax toxin
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interest.
Figures
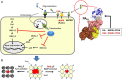
Comment on
-
Selective targeting of metastatic ovarian cancer using an engineered anthrax prodrug activated by membrane-anchored serine proteases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 12;119(28):e2201423119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201423119. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35867758 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Non-identity of the phospholipase of Bacillus anthracis with the anthrax toxin.J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Oct;15(2):261-5. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-2-261. J Gen Microbiol. 1956. PMID: 13376868 No abstract available.
-
Catalytically inactive anthrax toxin(s) are potential prophylactic agents.Vaccine. 2007 Dec 5;25(50):8410-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.09.063. Epub 2007 Oct 16. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17980467
-
Anthrax fusion protein therapy of cancer.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002 Aug;3(4):399-407. doi: 10.2174/1389203023380567. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002. PMID: 12370003 Review.
-
Anthrax Toxins in Context of Bacillus anthracis Spores and Spore Germination.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Aug 17;7(8):3167-78. doi: 10.3390/toxins7083167. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26287244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chemical basis of the virulence of Bacillus anthracis. VII. Two components of the anthrax toxin: their relationship to known immunising aggressins.Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Jun;37(3):263-71. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956. PMID: 13342351 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Anthrax meningoencephalitis: A case report.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Nov 1;29(1):9. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12759. eCollection 2025 Jan. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39563882 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax: Transmission, Pathogenesis, Prevention and Treatment.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jan 24;17(2):56. doi: 10.3390/toxins17020056. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39998073 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yamaizumi M., Mekada E., Uchida T., Okada Y., One molecule of diphtheria toxin fragment A introduced into a cell can kill the cell. Cell 15, 245–250 (1978). - PubMed
-
- Young J. A., Collier R. J., Anthrax toxin: Receptor binding, internalization, pore formation, and translocation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 243–265 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Duesbery N. S., et al. , Proteolytic inactivation of MAP-kinase-kinase by anthrax lethal factor. Science 280, 734–737 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

