Protective anti-gB neutralizing antibodies targeting two vulnerable sites for EBV-cell membrane fusion
- PMID: 35917353
- PMCID: PMC9371650
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2202371119
Protective anti-gB neutralizing antibodies targeting two vulnerable sites for EBV-cell membrane fusion
Abstract
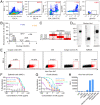
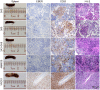
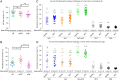
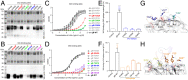
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects more than 90% of the world's adult population and accounts for a significant cancer burden of epithelial and B cell origins. Glycoprotein B (gB) is the primary fusogen essential for EBV entry into host cells. Here, we isolated two EBV gB-specific neutralizing antibodies, 3A3 and 3A5; both effectively neutralized the dual-tropic EBV infection of B and epithelial cells. In humanized mice, both antibodies showed effective protection from EBV-induced lymphoproliferative disorders. Cryoelectron microscopy analyses identified that 3A3 and 3A5 bind to nonoverlapping sites on domains D-II and D-IV, respectively. Structure-based mutagenesis revealed that 3A3 and 3A5 inhibit membrane fusion through different mechanisms involving the interference with gB-cell interaction and gB activation. Importantly, the 3A3 and 3A5 epitopes are major targets of protective gB-specific neutralizing antibodies elicited by natural EBV infection in humans, providing potential targets for antiviral therapies and vaccines.
Keywords: Epstein–Barr virus; glycoprotein B; lymphoproliferative disorder; neutralizing antibody; viral membrane fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
GB and gH/gL fusion machinery: a promising target for vaccines to prevent Epstein-Barr virus infection.Arch Virol. 2024 Jul 17;169(8):167. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06095-3. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 39020055 Review.
-
A Chimeric Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Presenting an Immunodominant Epitope of gB Elicited Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against EBV Infection In Vitro and In Vivo.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 May 7;17(18):26252-26262. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c00701. Epub 2025 Apr 24. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40272901
-
Rabbits immunized with Epstein-Barr virus gH/gL or gB recombinant proteins elicit higher serum virus neutralizing activity than gp350.Vaccine. 2016 Jul 25;34(34):4050-5. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.06.021. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27291087
-
A Neutralizing Antibody Targeting gH Provides Potent Protection against EBV Challenge In Vivo.J Virol. 2022 Apr 27;96(8):e0007522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00075-22. Epub 2022 Mar 29. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35348362 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein Barr Virus: Development of Vaccines and Immune Cell Therapy for EBV-Associated Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 8;12:734471. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.734471. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus gp42 antibodies reveal sites of vulnerability for receptor binding and fusion to B cells.Immunity. 2024 Mar 12;57(3):559-573.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.02.008. Immunity. 2024. PMID: 38479361 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Antibodies That Bind Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) gp350 and gH/gL and Shedding of EBV in Saliva From Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Multiplex Family Members in Taiwan.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 31;11(9):ofae464. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae464. eCollection 2024 Sep. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39229285 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus virions reveal species-specific tegument and envelope features.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0119424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01194-24. Epub 2024 Oct 29. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39470208 Free PMC article.
-
GB and gH/gL fusion machinery: a promising target for vaccines to prevent Epstein-Barr virus infection.Arch Virol. 2024 Jul 17;169(8):167. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06095-3. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 39020055 Review.
-
A Liposome-Based Nanoparticle Vaccine Induces Effective Immunity Against EBV Infection.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Mar 28;13(4):360. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13040360. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40338258 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

