Functional connectivity in the dorsal network of the cervical spinal cord is correlated with diffusion tensor imaging indices in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 35917721
- PMCID: PMC9421501
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103127
Functional connectivity in the dorsal network of the cervical spinal cord is correlated with diffusion tensor imaging indices in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
Abstract
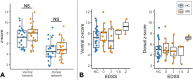
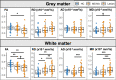
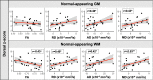
Focal lesions may affect functional connectivity (FC) of the ventral and dorsal networks in the cervical spinal cord of people with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). Resting-state FC can be measured using functional MRI (fMRI) at 3T. This study sought to determine whether alterations in FC may be related to the degree of damage in the normal-appearing tissue. Tissue integrity and FC in the cervical spinal cord were assessed with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and resting-state fMRI, respectively, in a group of 26 RRMS participants with high cervical lesion load, low disability, and minimally impaired sensorimotor function, and healthy controls. Lower fractional anisotropy (FA) and higher radial diffusivity (RD) were observed in the normal-appearing white matter in the RRMS group relative to controls. Average FC in ventral and dorsal networks was similar between groups. Significant associations were found between higher FC in the dorsal sensory network and several DTI markers of pathology in the normal-appearing tissue. In the normal-appearing grey matter, dorsal FC was positively correlated with axial diffusivity (AD) (r = 0.46, p = 0.020) and mean diffusivity (MD) (r = 0.43, p = 0.032). In the normal-appearing white matter, dorsal FC was negatively correlated with FA (r = -0.43, p = 0.028) and positively correlated with RD (r = 0.49, p = 0.012), AD (r = 0.42, p = 0.037) and MD (r = 0.53, p = 0.006). These results suggest that increased connectivity, while remaining within the normal range, may represent a compensatory mechanism in response to structural damage in support of preserved sensory function in RRMS.
Keywords: Diffusion tensor imaging; Functional connectivity; Multiple sclerosis; Resting-state fMRI; Spinal cord.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Baijot J., Denissen S., Costers L., Gielen J., Cambron M., D’Haeseleer M., D’hooghe M.B., Vanbinst A.-M., De Mey J., Nagels G., Van Schependom J. Signal quality as Achilles’ heel of graph theory in functional magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021;11(1) doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86792-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

