Design and Rationale of the HANSE Study: A Holistic German Lung Cancer Screening Trial Using Low-Dose Computed Tomography
- PMID: 35917826
- PMCID: PMC9708322
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1853-8291
Design and Rationale of the HANSE Study: A Holistic German Lung Cancer Screening Trial Using Low-Dose Computed Tomography
Abstract
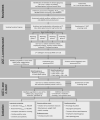
Despite the high prevalence and mortality of lung cancer and proven effectiveness of low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) to reduce mortality, Germany still lacks a national screening program. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) and the Federal Office for Radiation Protection (BfS) both published positive scientific evaluations recommending a quality-controlled national screening program. IQWiG underlined the importance of a clear risk definition, integrated smoking cessation programs, and quality assurance, highlighting the necessity of procedural optimization.In the HANSE study, former and current smokers aged 55-79 years are assessed for their lung cancer risk by the NELSON and PLCOM2012 risk scores. 5000 high-risk participants, defined as PLCOM2012 6-year risk ≥ 1.58 % or fulfilling NELSON risk inclusion criteria, will be screened by LDCT at baseline and after 12 months. Lung nodules are analyzed by a modified Lung-RADS 1.1 score of the HANSE study, and values of emphysema and coronary calcium are determined and randomly reported to the participants. 7100 low-risk participants serve as a control. All patients are followed-up for up to 10 years. The sensitivity and specificity of the two risk assessments and LDCT screening, effects of the randomized LDCT reporting, efficiency of lung nodule management, and several other factors are assessed to analyze the success and quality of the holistic screening program.The HANSE study is designed as a holistic lung cancer screening study in northern Germany to answer pressing questions for a successful implementation of an effective German lung cancer screening program. · HANSE is designed to address pressing questions for the implementation of lung cancer screening in Germany.. · HANSE compares NELSON and PLCOM2012 risk assessments for optimal definition of the high-risk group. . · HANSE integrates cardiac calcium and pulmonary emphysema scoring in a holistic screening approach.. CITATION FORMAT: · Vogel-Claussen J, Lasch F, Bollmann B et al. Design and Rationale of the HANSE Study: A Holistic German Lung Cancer Screening Trial Using Low-Dose Computed Tomography. Fortschr Röntgenstr 2022; 194: 1333 - 1345.
Trotz der hohen Prävalenz und Mortalität von Lungenkrebs und der nachgewiesenen Wirksamkeit von Niedrigdosis-Computertomografie (LDCT) zur Senkung der Mortalitätsrate existiert in Deutschland noch kein nationales Früherkennungsprogramm. Das Deutsche Institut für Qualität und Wirtschaftlichkeit im Gesundheitswesen (IQWiG) wie auch das Bundesamt für Strahlenschutz (BfS) haben positive wissenschaftliche Bewertungen mit Empfehlungen für ein qualitätskontrolliertes nationales Früherkennungsprogramm veröffentlicht. Das IQWiG betonte die Notwendigkeit klar definierter Risikokriterien, der Integration eines Rauchstoppprogramms sowie der Sicherstellung hoher Qualitätsstandards, was die Bedeutung von Prozessoptimierungen unterstreicht.In der HANSE-Studie werden ehemalige und aktive Raucher im Alter von 55–79 Jahren bezüglich ihres Lungenkrebsrisikos anhand der NELSON und PLCOM2012-Kriterien untersucht. 5000 Probanden mit hohem Risiko, definiert als PLCOM2012 6-Jahres-Risiko ≥ 1,58 % oder Erfüllen der NELSON-Kriterien, werden mittels LDCT zur Baseline sowie nach 12 Monaten untersucht. Lungenknötchen werden anhand eines modifizierten Lung-RADS 1.1 Scores der HANSE-Studie analysiert und zusätzlich Werte eines möglichen Lungenemphysems und koronaren Kalziums bestimmt und dem Befundbericht an die Probanden randomisiert beigefügt. 7100 Probanden mit niedrigem Risiko dienen als Kontrollgruppe. Alle Probanden werden für bis zu 10 Jahre nachverfolgt. Die Sensitivität und Spezifität der Risiko-Kriterien und der LDCT-Untersuchung, die Effekte der randomisierten LDCT-Befundbriefinhalte, die Effizienz des Knoten-Managements sowie weitere Parameter werden untersucht, um den Erfolg und die Qualität dieses holistischen Früherkennungsprogramms zu überprüfen.Die HANSE-Studie ist als holistische Lungenkrebs-Screening-Studie in Norddeutschland konzipiert und dient der Beantwortung drängender Fragen für eine erfolgreiche Implementierung eines Lungenkrebsfrüherkennungsprogramms in Deutschland. · Die HANSE-Studie ist als Vorreiter eines Früherkennungsprogramms für Lungenkrebs in Deutschland konzipiert.. · HANSE vergleicht die NELSON-Risikobewertung und den PLCOM2012-Score zur besseren Definition der Hochrisikogruppe.. · HANSE integriert koronares Kalzium-Scoring und den Lungenemphysem-Score in ein ganzheitliches Screening-Programm..
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commecial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have the following conflicts of interest:J. Vogel-Claussen: Research project support by BMBF, Siemens Healthineers, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline.Speaking fees by Boehringer Ingelheim, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Siemens Healthineers, Coreline Soft.M. Reck: Speaking and consulting fees by Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Beigene, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Lilly, Merck, MSD, Mirati, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi.B.A. Bollmann: Speaking fees by AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD, Bristol-Myers-Sqibb und Roche.G. Schmid-Bindert is an employee of AstraZeneca.The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of AI software tools for automated detection, quantification and categorization of pulmonary nodules in the HANSE LCS trial.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 13;14(1):27809. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78568-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39537690 Free PMC article.
-
[Statement paper on the implementation of a national organized program in Germany for the early detection of lung cancer in risk populations using low-dose CT screening including management of screening findings].Rofo. 2024 Feb;196(2):134-153. doi: 10.1055/a-2178-2846. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Rofo. 2024. PMID: 37816377 German.
-
Protocol and Rationale for the International Lung Screening Trial.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Apr;17(4):503-512. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201902-102OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020. PMID: 32011914 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening: Clinical evidence and implementation research.J Intern Med. 2022 Jul;292(1):68-80. doi: 10.1111/joim.13480. Epub 2022 Mar 24. J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35253286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening for Lung Cancer With Low-Dose Computed Tomography: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force.JAMA. 2021 Mar 9;325(10):971-987. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.0377. JAMA. 2021. PMID: 33687468
Cited by
-
ERS International Congress 2023: highlights from the Thoracic Oncology Assembly.ERJ Open Res. 2024 Feb 26;10(1):00860-2023. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00860-2023. eCollection 2024 Jan. ERJ Open Res. 2024. PMID: 38410708 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive surrogate markers of pulmonary hypertension are associated with poor survival in patients with cancer.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2024 Aug 22;11(1):e001916. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2023-001916. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39179271 Free PMC article.
-
Important steps towards a big change for lung health: a joint approach by the European Respiratory Society, the European Society of Radiology and their partners to facilitate implementation of the European Union's new recommendations on lung cancer screening.ERJ Open Res. 2023 May 9;9(3):00026-2023. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00026-2023. eCollection 2023 May. ERJ Open Res. 2023. PMID: 37228272 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of AI software tools for automated detection, quantification and categorization of pulmonary nodules in the HANSE LCS trial.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 13;14(1):27809. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78568-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39537690 Free PMC article.
-
Strengthening lung cancer screening in Europe: fostering participation, improving outcomes, and addressing health inequalities through collaborative initiatives in the SOLACE consortium.Insights Imaging. 2024 Oct 22;15(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01814-5. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39436577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes B, Kraywinkel K, Nowossadeck E et al.Bericht zum Krebsgeschehen in Deutschland. Robert Koch-Institut Gesundheitsberichterstattung-Hefte. 2016 doi: 10.17886/rkipubl-2016-014. - DOI
-
- Krebs in Deutschland für 2015/2016. 12. Ausgabe. Robert Koch-Institut (Hrsg.) und die Gesellschaft der epidemiologischen Krebsregister in Deutschland e. V. (Hrsg). Berlin, 2019. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

