Evaluating the immunogenicity of gold nanoparticles conjugated RBD with Freund's adjuvant as a potential vaccine against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35917987
- PMCID: PMC9339102
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105687
Evaluating the immunogenicity of gold nanoparticles conjugated RBD with Freund's adjuvant as a potential vaccine against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Background: and Introduction: SARS-CoV-2 is currently considered as the most challenging issue in the field of health and medicine by causing a global pandemic. Vaccines are counted as a promising candidate to terminate this deadly pandemic. Various structural proteins in SARS-CoV-2 have recently drawn attention to be utilized as candidate vaccines to stimulate immune responses against COVID-19.
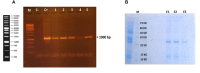
Materials and methods: In current study, the RBD protein was cloned and expressed in E. coli host. Then, the expressed RBD protein was purified and its characterizations were evaluated through various methods. Gold nanoparticles, which were utilized as a carrier for candidate Nano-vaccine, were synthesized via oxidation-reduction reaction. While Gold NPs-conjugated RBD was injected into the second treatment group, in the first candidate vaccine, RBD was injected into the first treatment group solely. Complete and Incomplete Freud's Adjuvant were also utilized for both treatment groups to enhance the immune responses against RBD antigen. Immunizations were repeated 2 times in 14-day intervals to boost the immune system of BALB/c mice. The humoral and cell-mediated immune responses were examined through immune and cytokine assays.
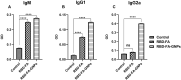
Results: Our outcomes demonstrate that strong short-term humoral immunity (IgM) was induced in both the first and second treatment group, while long-term humoral responses (IgG) were only observed in the second treatment group. While stronger short- and long-term humoral (IgM and IgG, respectively) were observed in the second treatment group, particular cytokines production (TNF-ɑ and IFN-γ) as a marker of cell-mediated responses were significantly higher in the first treatment group.
Discussion and conclusion: Our study results show the high potentiality of RBD protein as an appropriate stimulating antigen in vaccine synthesis and testifies RBD-based candidate vaccines to control the COVID-19 pandemic. Our outcomes also recommend that Nano-vaccines can be more suitable candidates when stronger long-term immune responses matter.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; Freund's adjuvant; Gold nanoparticles; Immunogenic proteins; Nano-vaccines; RBD protein; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Influence of Adjuvant Type on the Immunogenicity of RBD/N Cocktail Antigens as a Vaccine Candidate against SARS-CoV-2 Virus.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0256422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02564-22. Epub 2023 May 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37199661 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant COVID-19 vaccine based on recombinant RBD/Nucleoprotein and saponin adjuvant induces long-lasting neutralizing antibodies and cellular immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 8;13:974364. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.974364. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36159845 Free PMC article.
-
A SARS-CoV-2 vaccine based on conjugation of SARS-CoV-2 RBD with IC28 peptide and mannan.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Dec 1;222(Pt A):661-670. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.180. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 36152702 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Assembling protein nanoparticle platform for multivalent antigen delivery in vaccine development.Int J Pharm. 2025 May 15;676:125597. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125597. Epub 2025 Apr 13. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40233885 Review.
-
Innovative vaccine platforms against infectious diseases: Under the scope of the COVID-19 pandemic.Int J Pharm. 2021 Dec 15;610:121212. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121212. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34687816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Updates on the Biofunctionalization of Gold Nanoparticles for the Rapid and Sensitive Multiplatform Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Its Proteins: From Computational Models to Validation in Human Samples.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 25;24(11):9249. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119249. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unglycosylated Soluble SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) Produced in E. coli Combined with the Army Liposomal Formulation Containing QS21 (ALFQ) Elicits Neutralizing Antibodies against Mismatched Variants.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;11(1):42. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11010042. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36679887 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles and Antiviral Vaccines.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Dec 27;12(1):30. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12010030. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38250843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccination as a Promising Approach in Cardiovascular Risk Mitigation: Are We Ready to Embrace a Vaccine Strategy?Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 20;14(12):1637. doi: 10.3390/biom14121637. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766344 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lan J., Ge J., Yu J., Shan S., Zhou H., Fan S., Zhang Q., Shi X., Wang Q., Zhang L. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature. 2020;581(7807):215–220. - PubMed
-
- Jebril, N., World Health Organization Declared a Pandemic Public Health Menace: A Systematic Review of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 “COVID-19”, up to 26th March 2020. Available at: SSRN 3566298 2020.
-
- Worldmeters Coronavirus update. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/(accessed 01 December 2021).
-
- Paules C.I., Marston H.D., Fauci A.S. Coronavirus infections—more than just the common cold. JAMA. 2020;323(8):707–708. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

