Urinary HER2, TWEAK and VCAM-1 levels are associated with new-onset proteinuria in paediatric lupus nephritis
- PMID: 35918102
- PMCID: PMC9351344
- DOI: 10.1136/lupus-2022-000719
Urinary HER2, TWEAK and VCAM-1 levels are associated with new-onset proteinuria in paediatric lupus nephritis
Abstract
Objective: Lupus nephritis is a key driver of morbidity and mortality in SLE. Detecting active nephritis on a background of pre-existing renal damage is difficult, leading to potential undertreatment and accumulating injury. An unmet need is a biomarker that distinguishes active lupus nephritis, particularly important in paediatrics where minimising invasive procedures is desirable.
Methods: This was a multicentre, prospective study of 113 paediatric patients with biopsy-proven lupus nephritis. Clinical data and urine were obtained every 3-4 months and patients averaged 2 years on study with seven time points. Urine was analysed for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), tumour necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) by ELISA. We defined active disease as either a rise in serum creatinine ≥0.3 mg/dL from baseline or a rise in renal Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index score from the previous visit. These markers were also studied in patients with acute kidney injury, juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), amplified pain syndrome and healthy controls.
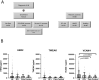
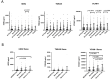
Results: The rate of active disease was 56% over an average of 2 years of follow-up. HER2 and VCAM-1 were significantly elevated at time points with active disease defined by increased serum creatinine compared with time points with inactive disease or patients who never flared. All three biomarkers were associated with new-onset proteinuria and VCAM-1 was elevated at time points preceding new-onset proteinuria. These biomarkers were not increased in acute kidney injury or JIA.
Conclusion: All three biomarkers were associated with new onset proteinuria and increased VCAM-1 may predict impending proteinuria. These biomarkers provide potential non-invasive measures for monitoring that may be more sensitive to impending flare than conventional measures.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; autoimmunity; lupus nephritis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: LES is associate editor for Lupus Science & Medicine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Urine ALCAM, PF4 and VCAM-1 Surpass Conventional Metrics in Identifying Nephritis Disease Activity in Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2022 May 26;13:885307. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.885307. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720325 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary angiostatin, CXCL4 and VCAM-1 as biomarkers of lupus nephritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Jan 11;20(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1498-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29325582 Free PMC article.
-
Clinico-pathological associations of serum VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 levels in patients with lupus nephritis.Lupus. 2021 Jun;30(7):1039-1050. doi: 10.1177/09612033211004727. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Lupus. 2021. PMID: 33765901
-
Prognostic and Diagnostic Values of Novel Serum and Urine Biomarkers in Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review.Am J Nephrol. 2021;52(7):559-571. doi: 10.1159/000517852. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Am J Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34515043
-
Urinary biomarkers in lupus nephritis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011 Jun;40(3):138-50. doi: 10.1007/s12016-010-8197-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 20127204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary MCP-1 and VCAM-1 as non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis and activity assessment of lupus nephritis.PLoS One. 2025 May 19;20(5):e0323334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323334. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40388387 Free PMC article.
-
Flares in Lupus Nephritis: Risk Factors and Strategies for Their Prevention.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2023 Oct;25(10):183-191. doi: 10.1007/s11926-023-01109-6. Epub 2023 Jul 15. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37452914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin receptor blockers modulate the lupus CD4+ T cell epigenome characterized by TNF family-linked signaling.JCI Insight. 2024 Dec 17;10(3):e176811. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.176811. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39688922 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-ErbB2 dual kinase inhibitor lapatinib decreases autoantibody levels and worsens renal disease in Interferon α-accelerated murine lupus.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Oct 25;140:112692. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112692. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39079344 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
