Monoclonal antibodies to lipoarabinomannan/arabinomannan - characteristics and implications for tuberculosis research and diagnostics
- PMID: 35918247
- PMCID: PMC9771891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2022.07.001
Monoclonal antibodies to lipoarabinomannan/arabinomannan - characteristics and implications for tuberculosis research and diagnostics
Abstract
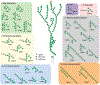
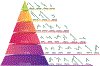
Antibodies to the mycobacterial surface lipoglycan lipoarabinomannan (LAM) and its related capsular polysaccharide arabinomannan (AM) are increasingly important for investigations focused on both understanding mechanisms of protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and developing next-generation point-of-care tuberculosis (TB) diagnostics. We provide here an overview of the growing pipeline of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to LAM/AM. Old and new methodologies for their generation are reviewed and we outline and discuss their glycan epitope specificity and other features with implications for the TB field.
Keywords: antigen–antibody interactions; biomarker; glycans; lipoglycans; mycobacteria; oligosaccharides; point-of-care tests.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests No interests are declared.
Figures

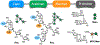
Similar articles
-
Generation of mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan-specific monoclonal antibodies and their ability to identify mycobacterium isolates.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021 Jun;54(3):437-446. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.005. Epub 2020 Feb 20. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021. PMID: 32146163
-
Monoclonal antibodies from humans with Mycobacterium tuberculosis exposure or latent infection recognize distinct arabinomannan epitopes.Commun Biol. 2021 Oct 12;4(1):1181. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02714-w. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34642445 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Sensitive Immunoassay Targeting the 5-Methylthio-d-Xylofuranose-Lipoarabinomannan Epitope Meets the WHO's Performance Target for Tuberculosis Diagnosis.J Clin Microbiol. 2018 Nov 27;56(12):e01338-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01338-18. Print 2018 Dec. J Clin Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30257899 Free PMC article.
-
Application of lipoarabinomannan antigen in tuberculosis diagnostics: current evidence.Postgrad Med J. 2014 Mar;90(1061):155-63. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2013-132053. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Postgrad Med J. 2014. PMID: 24429376 Review.
-
Lipoarabinomannan, and its related glycolipids, induce divergent and opposing immune responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis depending on structural diversity and experimental variations.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016 Jan;96:120-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.09.005. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016. PMID: 26586646 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective Glycan Labeling of Mannose-Containing Glycolipids in Mycobacteria.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Jan 10;146(1):377-385. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c09495. Epub 2023 Dec 19. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38112296 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world diagnostic accuracy of lipoarabinomannan in three non-sputum biospecimens for pulmonary tuberculosis disease.EBioMedicine. 2024 Oct;108:105353. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105353. Epub 2024 Sep 26. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39332390 Free PMC article.
-
Collected Thoughts on Mycobacterial Lipoarabinomannan, a Cell Envelope Lipoglycan.Pathogens. 2023 Oct 26;12(11):1281. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111281. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Glycolipids on the CD4+ T Cell-Macrophage Immunological Synapse.J Immunol. 2023 Nov 1;211(9):1385-1396. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300107. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37695687 Free PMC article.
-
Blazing the trail for innovative tuberculosis diagnostics.Infection. 2024 Feb;52(1):29-42. doi: 10.1007/s15010-023-02135-3. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Infection. 2024. PMID: 38032537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021, License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
-
- Schrager LK, et al. (2020) The status of tuberculosis vaccine development. Lancet Infect Dis 20, e28–e37 - PubMed
-
- Mangtani P, et al. (2014) Protection by BCG vaccine against tuberculosis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Clin Infect Dis 58, 470–480 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

