Spatiotemporal control of engineered bacteria to express interferon-γ by focused ultrasound for tumor immunotherapy
- PMID: 35918309
- PMCID: PMC9345953
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31932-x
Spatiotemporal control of engineered bacteria to express interferon-γ by focused ultrasound for tumor immunotherapy
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Spatiotemporal control of engineered bacteria to express interferon-γ by focused ultrasound for tumor immunotherapy.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 30;15(1):3656. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48061-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38688906 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
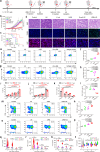
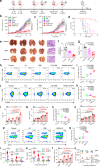
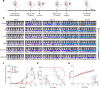
Bacteria-based tumor therapy has recently attracted wide attentions due to its unique capability in targeting tumors and preferentially colonizing the core area of the tumor. Various therapeutic genes are also harbored into these engineering bacteria to enhance their anti-tumor efficacy. However, it is difficult to spatiotemporally control the expression of these inserted genes in the tumor site. Here, we engineer an ultrasound-responsive bacterium (URB) which can induce the expression of exogenous genes in an ultrasound-controllable manner. Owing to the advantage of ultrasound in tissue penetration, an acoustic remote control of bacterial gene expression can be realized by designing a temperature-actuated genetic switch. Cytokine interferon-γ (IFN-γ), an important immune regulatory molecule that plays a significant role in tumor immunotherapy, is used to test the system. Our results show that brief hyperthermia induced by focused ultrasound promotes the expression of IFN-γ gene, improving anti-tumor efficacy of URB in vitro and in vivo. Our study provides an alternative strategy for bacteria-mediated tumor immunotherapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-visible engineered bacteria for tumor chemo-immunotherapy.Cell Rep Med. 2024 May 21;5(5):101512. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101512. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38640931 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-controllable engineered bacteria for cancer immunotherapy.Nat Commun. 2022 Mar 24;13(1):1585. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29065-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35332124 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal-responsive ultrasound activatable in situ production of therapeutics for real-time imaging and targeted tumor therapy.Theranostics. 2025 Mar 18;15(9):4212-4228. doi: 10.7150/thno.101714. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40213677 Free PMC article.
-
New strategies for active immunotherapy with genetically engineered tumor cells.Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Oct;4(5):619-23. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90037-f. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1418729 Review.
-
Bacteria-Based Cancer Immunotherapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Feb 10;8(7):2003572. doi: 10.1002/advs.202003572. eCollection 2021 Apr. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 33854892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-pathogenic E. coli displaying decoy-resistant IL18 mutein boosts anti-tumor and CAR NK cell responses.Nat Biotechnol. 2025 Aug;43(8):1311-1323. doi: 10.1038/s41587-024-02418-6. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Nat Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39367093
-
MOTS-c: A promising mitochondrial-derived peptide for therapeutic exploitation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 25;14:1120533. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1120533. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36761202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in application of nanomedicines for enhancing cancer sono-immunotherapy.Ultrason Sonochem. 2024 Dec;111:107105. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.107105. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Ultrason Sonochem. 2024. PMID: 39427436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What Is the Magical Cavitation Bubble: A Holistic Perspective to Trigger Advanced Bubbles, Nano-Sonocatalysts, and Cellular Sonosensitizers.BME Front. 2024 Sep 19;5:0067. doi: 10.34133/bmef.0067. eCollection 2024. BME Front. 2024. PMID: 39301016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering bacteria as interactive cancer therapies.Science. 2022 Nov 25;378(6622):858-864. doi: 10.1126/science.add9667. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Science. 2022. PMID: 36423303 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

