Acute orexin antagonism selectively modulates anticipatory anxiety in humans: implications for addiction and anxiety
- PMID: 35918313
- PMCID: PMC9345881
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-022-02090-x
Acute orexin antagonism selectively modulates anticipatory anxiety in humans: implications for addiction and anxiety
Abstract
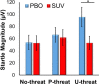
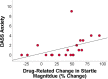
Research indicates that heightened anticipatory anxiety underlies several forms of psychopathology. Anticipatory anxiety can be reliably and objectively measured in the laboratory using the No-Predictable-Unpredictable (NPU) threat paradigm. The NPU paradigm is an ideal research tool for the NIH 'Fast-Fail' approach of screening promising compounds and testing human target engagement. Evidence from preclinical studies suggests that the hypocretin/orexin (ORX) hypothalamic neuropeptide system is a potential means for modulating anticipatory anxiety and disrupting stress-related alcohol use. The current study tested this question using a psychophysiological probe of the ORX system in humans. We examined whether a single dose of suvorexant (SUV; 10 mg; dual ORX receptor antagonist) can effectively and selectively target a well-validated human laboratory index of exaggerated anticipatory anxiety using a within-subjects placebo-controlled design. A total of twenty-one volunteers completed two laboratory sessions during acute administration of 10 mg SUV or placebo. Across sessions, we administered the NPU paradigm probing sustained anticipatory anxiety and fear while startle eyeblink was recorded as an index of aversive reactivity. Questionnaires assessing mood states and subjective drug effects were also collected. Results indicated SUV was well-tolerated. Compared with placebo, SUV was associated with decreased startle reactivity during anticipatory anxiety but not fear or no-threat conditions. Therefore, SUV selectively and effectively reduced objective indicators of anticipatory anxiety in humans and engaged our laboratory target of psychopathology. ORX antagonism may be a promising strategy for modulating human anxiety and potentially, stress-related alcohol use.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of handgun ownership and biological sex on startle reactivity to predictable and unpredictable threats.Int J Psychophysiol. 2024 Mar;197:112297. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2024.112297. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Int J Psychophysiol. 2024. PMID: 38185419 Free PMC article.
-
The novel vasopressin receptor (V1aR) antagonist SRX246 reduces anxiety in an experimental model in humans: a randomized proof-of-concept study.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Sep;238(9):2393-2403. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05861-4. Epub 2021 May 10. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33970290 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Assessing fear and anxiety in humans using the threat of predictable and unpredictable aversive events (the NPU-threat test).Nat Protoc. 2012 Feb 23;7(3):527-32. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.001. Nat Protoc. 2012. PMID: 22362158 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of startle reactivity to unpredictable threat on the relation between bullying victimization and internalizing psychopathology.J Psychiatr Res. 2019 Dec;119:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2019.09.004. Epub 2019 Sep 6. J Psychiatr Res. 2019. PMID: 31520836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hypocretin/orexin system as a target for excessive motivation in alcohol use disorders.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Jun;235(6):1663-1680. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4871-2. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29508004 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lateral hypothalamus orexinergic projection to the medial prefrontal cortex modulates chronic stress-induced anhedonia but not anxiety and despair.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Mar 16;14(1):149. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02860-9. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38493173 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin receptors: possible therapeutic targets for psychiatric disorders.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Aug;242(8):1669-1691. doi: 10.1007/s00213-025-06767-1. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40153060 Review.
-
The Orexin/Hypocretin System, the Peptidergic Regulator of Vigilance, Orchestrates Adaptation to Stress.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 17;12(2):448. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020448. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Embryonic ethanol exposure and optogenetic activation of hypocretin neurons stimulate similar behaviors early in life associated with later alcohol consumption.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 6;14(1):3021. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52465-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38321123 Free PMC article.
-
What evidence is there for implicating the brain orexin system in neuropsychiatric symptoms in dementia?Front Psychiatry. 2022 Nov 25;13:1052233. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1052233. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36506416 Free PMC article.

