Understanding hesitancy with revealed preferences across COVID-19 vaccine types
- PMID: 35918372
- PMCID: PMC9345393
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-15633-5
Understanding hesitancy with revealed preferences across COVID-19 vaccine types
Abstract
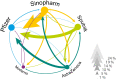
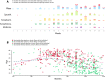
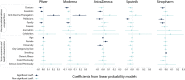
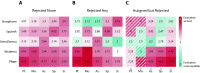
Many countries have secured larger quantities of COVID-19 vaccines than their population is willing to take. The abundance and the large variety of vaccines created not only an unprecedented intensity of vaccine related public discourse, but also a historical moment to understand vaccine hesitancy better. Yet, the heterogeneity of hesitancy by vaccine types has been neglected in the existing literature so far. We address this problem by analysing the acceptance and the assessment of five vaccine types. We use information collected with a nationally representative survey at the end of the third wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in Hungary. During the vaccination campaign, individuals could reject the assigned vaccine to wait for a more preferred alternative that enables us to quantify revealed preferences across vaccine types. We find that hesitancy is heterogenous by vaccine types and is driven by individuals' trusted source of information. Believers of conspiracy theories are more likely to evaluate the mRNA vaccines (Pfizer and Moderna) unacceptable. Those who follow the advice of politicians are more likely to evaluate vector-based (AstraZeneca and Sputnik) or whole-virus vaccines (Sinopharm) acceptable. We argue that the greater selection of available vaccine types and the free choice of the individual are desirable conditions to increase the vaccination rate in societies.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

