PPAR-γ alleviates the inflammatory response in TNF-α-induced fibroblast-like synoviocytes by binding to p53 in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 35918412
- PMCID: PMC9889328
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-022-00957-9
PPAR-γ alleviates the inflammatory response in TNF-α-induced fibroblast-like synoviocytes by binding to p53 in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
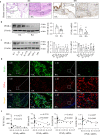
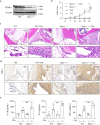
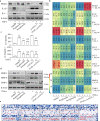
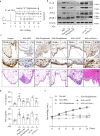
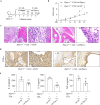
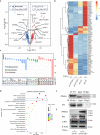
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by synovial inflammation, synoviocyte expansion and damage to cartilage and bone. We recently reported that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ inhibited the proliferation and activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), and was downregulated in RA synovial. In this study we investigated the role of PPAR-γ in RA and the underlying mechanisms. Adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) was induced in rats; from D15, AIA rats were orally administered pioglitazone (30 mg·kg-1·d-1) or rosiglitazone (4 mg·kg-1·d-1) for 14 days. Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) was induced in wild-type and Ppar-γ+/- mice. We showed that the expression of PPAR-γ was significantly reduced, whereas that of TNF-α was markedly increased in human RA FLS. In CIA mice, knockdown of PPAR-γ expression (Ppar-γ+/-) aggravated the ankle inflammation. Similarly, T0070907 (a PPAR-γ antagonist) or si-PPAR-γ promoted the activation and inflammation of TNF-α-induced FLS in vitro. On the contrary, administration of PPAR-γ agonist pioglitazone or rosiglitazone, or injection of ad-Ppar-γ into the ankle of AIA rat in vivo induced overexpression of PPAR-γ, reduced the paw swelling and inflammation, and downregulated activation and inflammation of FLS in RA. Interesting, injection of ad-Ppar-γ into the ankle also reversed the ankle inflammation in Ppar-γ+/- CIA mice. We conducted RNA-sequencing and KEGG pathway analysis, and revealed that PPAR-γ overexpression was closely related to p53 signaling pathway in TNF-α-induced FLS. Co-IP study confirmed that p53 protein was bound to PPAR-γ in RA FLS. Taken together, PPAR-γ alleviates the inflammatory response of TNF-α-induced FLS by binding p53 in RA.
Keywords: PPAR-γ; adjuvant-induced arthritis; collagen-induced arthritis; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; inflammatory response; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

