Sexually transmitted infections and female reproductive health
- PMID: 35918418
- PMCID: PMC9362696
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-022-01177-x
Sexually transmitted infections and female reproductive health
Abstract
Women are disproportionately affected by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) throughout life. In addition to their high prevalence in women, STIs have debilitating effects on female reproductive health due to female urogenital anatomy, socio-cultural and economic factors. In this Review, we discuss the prevalence and impact of non-HIV bacterial, viral and parasitic STIs on the reproductive and sexual health of cisgender women worldwide. We analyse factors affecting STI prevalence among transgender women and women in low-income settings, and describe the specific challenges and barriers to improved sexual health faced by these population groups. We also synthesize the latest advances in diagnosis, treatment and prevention of STIs.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
O.T.V.G. has received research grant support from Gilead Sciences, Inc. and Abbott Molecular, and serves on the scientific advisory board for Scynexis. C.A.M. has received research grant support from Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Gilead Sciences, Inc. and Abbott Molecular, is a consultant for Cepheid, Scynexis, Lupin Pharmaceuticals, PhagoMed and BioFire Diagnostics, and has received honoraria from Elsevier, Abbott Molecular, Cepheid, Becton Dickinson, Roche Diagnostics and Lupin. J.M. serves on scientific advisory committees for Merck and Gilead, has received research grant support from Becton Dickinson and GlaxoSmithKline, and serves as a scientific advisor for OSEL.
Figures

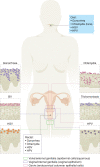
References
-
- Reported STDs reach all-time high for 6th consecutive year. CDC (3 April 2021); https://www.cdc.gov/nchhstp/newsroom/2021/2019-std-surveillance-report-p...
-
- CDC Fact Sheet: 10 Ways STDs Impact Women Differently from Men (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2011); https://www.cdc.gov/std/health-disparities/stds-women-042011.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

