Targeted delivery of irinotecan to colon cancer cells using epidermal growth factor receptor-conjugated liposomes
- PMID: 35918704
- PMCID: PMC9344698
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-022-01012-8
Targeted delivery of irinotecan to colon cancer cells using epidermal growth factor receptor-conjugated liposomes
Abstract
Background: CPT-11 (irinotecan) is one of the most efficient agents used for colorectal cancer chemotherapy. However, as for many other chemotherapeutic drugs, how to minimize the side effects of CPT-11 still needs to be thoroughly described.
Objectives: This study aimed to develop the CPT-11-loaded DSPE-PEG 2000 targeting EGFR liposomal delivery system and characterize its targeting specificity and therapeutic effect on colorectal cancer (CRC) cells in vitro and in vivo.
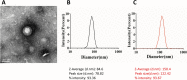
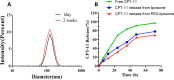
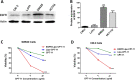
Results: The synthesized liposome exhibited spherical shapes (84.6 ± 1.2 nm to 150.4 nm ± 0.8 nm of estimated average sizes), good stability, sustained release, and enough drug loading (55.19%). For in vitro experiments, SW620 cells treated with CPT-11-loaded DSPE-PEG2000 targeting EGFR liposome showed lower survival extended level of intracellular ROS production. In addition, it generated an enhanced apoptotic cell rate by upregulating the protein expression of both cleaved-caspase-3 and cleaved-caspase-9 compared with those of SW620 cells treated with free CPT-11. Importantly, the xenograft model showed that both the non-target and EGFR-targeted liposomes significantly inhibited tumor growth compared to free CPT-11.
Conclusions: Compared with the non-target CPT-11-loaded DSPE-PEG2000 liposome, CPT-11-loaded DSPE-PEG2000 targeting EGFR liposome treatment showed much better antitumor activity in vitro in vivo. Thus, our findings provide new assets and expectations for CRC targeting therapy.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; DSPE-PEG2000; EGFR; Irinotecan (CPT-11); SW620 cell.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Preparation of irinotecan-loaded folate-targeted liposome for tumor targeting delivery and its antitumor activity.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012 Sep;13(3):802-10. doi: 10.1208/s12249-012-9776-5. Epub 2012 May 26. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012. PMID: 22639238 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable Thermo-Sensitive Chitosan Hydrogel Containing CPT-11-Loaded EGFR-Targeted Graphene Oxide and SLP2 shRNA for Localized Drug/Gene Delivery in Glioblastoma Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 26;21(19):7111. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197111. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32993166 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of trapping agents on the antitumor efficacy of irinotecan liposomes: head-to-head comparison of ammonium sulfate, sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin and sucrose octasulfate.Biomater Sci. 2018 Dec 18;7(1):419-428. doi: 10.1039/c8bm01175c. Biomater Sci. 2018. PMID: 30500018
-
Integration of novel agents in the treatment of colorectal cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2004 Sep;54 Suppl 1:S32-9. doi: 10.1007/s00280-004-0884-0. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15309512 Review.
-
Effective prodrug liposome and conversion to active metabolite.Curr Drug Metab. 2000 Jul;1(1):31-48. doi: 10.2174/1389200003339225. Curr Drug Metab. 2000. PMID: 11467079 Review.
Cited by
-
Nano-Radiopharmaceuticals in Colon Cancer: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 14;18(2):257. doi: 10.3390/ph18020257. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of key extracellular proteins as the potential biomarkers in thyroid eye disease.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 29;20(4):e0322415. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322415. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40299971 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advanced lipid-based nanomedicines for overcoming cancer resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Jun 21;7:24. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.19. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39050885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanocarriers for Anticancer Drug Delivery.Polymers (Basel). 2023 May 16;15(10):2317. doi: 10.3390/polym15102317. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative Nanoparticulate Strategies in Colon Cancer Treatment: A Paradigm Shift.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Mar 1;25(3):52. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02759-0. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38429601 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

