Targeting microglial autophagic degradation of the NLRP3 inflammasome for identification of thonningianin A in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 35918778
- PMCID: PMC9347127
- DOI: 10.1186/s41232-022-00209-7
Targeting microglial autophagic degradation of the NLRP3 inflammasome for identification of thonningianin A in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
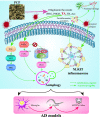
Background: NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation plays a critical role in the pathogenesis and development of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Microglial autophagic degradation not only decreases the deposits of extracellular Aβ fibrils but also inhibits the activation of NRLP3 inflammasome. Here, we aimed to identify the potent autophagy enhancers from Penthorum chinense Pursh (PCP) that alleviate the pathology of AD via inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome.
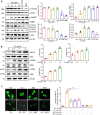
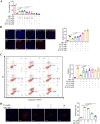
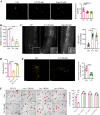
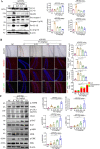
Methods: At first, autophagic activity-guided isolation was performed to identify the autophagy enhancers in PCP. Secondly, the autophagy effect was monitored by detecting LC3 protein expression using Western blotting and the average number of GFP-LC3 puncta per microglial cell using confocal microscopy. Then, the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome was measured by detecting the protein expression and transfected fluorescence intensity of NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1, as well as the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. Finally, the behavioral performance was evaluated by measuring the paralysis in C. elegans, and the cognitive function was tested by Morris water maze (MWM) in APP/PS1 mice.
Results: Four ellagitannin flavonoids, including pinocembrin-7-O-[4″,6″-hexahydroxydiphenoyl]-glucoside (PHG), pinocembrin-7-O-[3″-O-galloyl-4″,6″-hexahydroxydiphenoyl]-glucoside (PGHG), thonningianin A (TA), and thonningianin B (TB), were identified to be autophagy enhancers in PCP. Among these, TA exhibited the strongest autophagy induction effect, and the mechanistic study demonstrated that TA activated autophagy via the AMPK/ULK1 and Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways. In addition, TA effectively promoted the autophagic degradation of NLRP3 inflammasome in Aβ(1-42)-induced microglial cells and ameliorated neuronal damage via autophagy induction. In vivo, TA activated autophagy and improved behavioral symptoms in C. elegans. Furthermore, TA might penetrate the blood-brain barrier and could improve cognitive function and ameliorate the Aβ pathology and the NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation via the AMPK/ULK1 and Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways in APP/PS1 mice.
Conclusion: We identified TA as a potent microglial autophagy enhancer in PCP that promotes the autophagic degradation of the NLRP3 inflammasome to alleviate the pathology of AD via the AMPK/ULK1 and Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways, which provides novel insights for TA in the treatment of AD.
Keywords: AMPK/ULK1; Alzheimer’s disease; Autophagy; NLRP3 inflammasome; Raf/MEK/ERK; Thonningianin A.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Cao YW, Jiang Y, Zhang DY, Zhang XJ, Hu YJ, Li P, Su H, Wan JB. The hepatoprotective effect of aqueous extracts of Penthorum chinense Pursh against acute alcohol-induced liver injury is associated with ameliorating hepatic steatosis and reducing oxidative stress. Food Funct. 2015;6(5):1510–1517. doi: 10.1039/C5FO00098J. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

