Unexpected pulmonary edema and cardiac arrest following wedge resection of spontaneous pneumothorax -A case report
- PMID: 35918863
- PMCID: PMC9346198
- DOI: 10.17085/apm.21116
Unexpected pulmonary edema and cardiac arrest following wedge resection of spontaneous pneumothorax -A case report
Abstract
Background: Reexpansion pulmonary edema is a rare but potentially lethal complication. We report a case of suspected reexpansion pulmonary edema that led to cardiac arrest.
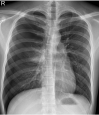
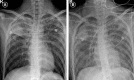
Case: A 16-year-old male patient underwent wedge resection due to right pneumothorax. The patient showed pink frothy sputum three hours following surgery, and a chest x-ray showed right unilateral pulmonary edema. Thirteen hours following surgery, the patient continuously showed pink frothy sputum and presented with severe hypoxemia, tachypnea, and tachycardia. After transferring to the intensive care unit (ICU), he developed ventricular tachycardia. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation was performed for 32 min. Chest X-ray showed diffuse bilateral pulmonary edema. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was performed. During the 65 days of ICU care, the patient became mentally alert. However, follow-up echocardiography revealed severe heart failure.
Conclusions: Rexpansion pulmonary edema can rapidly progress to diffuse bilateral pulmonary edema. Therefore, careful observation is required for the patients who show signs of pulmonary edema after reexpansion.
Keywords: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; Heart arrest; Pneumothorax; Pulmonary edema.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Sugiyama Y, Shimizu F, Shimizu S, Urasawa M, Tanaka S, Kawamata M. Severe re-expansion pulmonary edema induced by one-lung ventilation. Respir Care. 2015;60:e134–40. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya M, Kallet RH, Ware LB, Matthay MA. Negative-pressure pulmonary edema. Chest. 2016;150:927–33. - PubMed
-
- Righini M, Robert-Ebadi H. Diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism. Hamostaseologie. 2018;38:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Sherman SC. Reexpansion pulmonary edema: a case report and review of the current literature. J Emerg Med. 2003;24:23–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

