Aligned peptoid-based macrodiscs for structural studies of membrane proteins by oriented-sample NMR
- PMID: 35918898
- PMCID: PMC9463639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.07.024
Aligned peptoid-based macrodiscs for structural studies of membrane proteins by oriented-sample NMR
Abstract
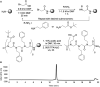
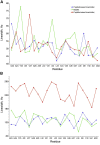
Development of a robust, uniform, and magnetically orientable lipid mimetic will undoubtedly advance solid-state NMR of macroscopically aligned membrane proteins. Here, we report on a novel lipid membrane mimetic based on peptoid belts. The peptoids, composed of 15 residues, were synthesized by alternating N-(2-phenethyl)glycine with N-(2-carboxyethyl)glycine residues at a 2:1 molar ratio. The chemically synthesized peptoids possess a much lower degree of polydispersity versus styrene-maleic acid polymers, thus yielding uniform discs. Moreover, the peptoid oligomers are more flexible and do not require a specific folding, unlike lipoproteins, in order to wrap around the hydrophobic membrane core. The NMR spectra measured for the membrane-bound form of Pf1 coat protein incorporated in this new lipid mimetics demonstrate a higher order parameter and uniform linewidths compared with the conventional bicelles and peptide-based macrodiscs. Importantly, unlike bicelles, the peptoid-based macrodiscs are detergent free.
Copyright © 2022 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Peptoid-based macrodiscs of variable lipid composition for structural studies of membrane proteins by oriented-sample solid-state NMR.J Struct Biol X. 2023 Dec 8;9:100095. doi: 10.1016/j.yjsbx.2023.100095. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Struct Biol X. 2023. PMID: 38094992 Free PMC article.
-
Macrodiscs Comprising SMALPs for Oriented Sample Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy of Membrane Proteins.Biophys J. 2018 Jul 3;115(1):22-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.05.024. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29914645 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane proteins in magnetically aligned phospholipid polymer discs for solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Sep 1;1862(9):183333. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183333. Epub 2020 May 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32371072 Free PMC article.
-
Nanodiscs versus macrodiscs for NMR of membrane proteins.Biochemistry. 2011 Oct 25;50(42):8983-5. doi: 10.1021/bi201289c. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21936505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond detergent micelles: The advantages and applications of non-micellar and lipid-based membrane mimetics for solution-state NMR.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2019 Oct-Dec;114-115:271-283. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2019. PMID: 31779883 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of nanodisc-forming peptides for membrane protein studies.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 Jan;653(Pt B):1402-1414. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.09.162. Epub 2023 Sep 29. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024. PMID: 37801850 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the stability and homogeneity of non-ionic polymer nanodiscs by tuning electrostatic interactions.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023 Mar 15;634:887-896. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.12.112. Epub 2022 Dec 21. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023. PMID: 36566634 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the Optimal Molecular Characteristics of Hydrophobe-Containing Polypeptoids to Induce Liposome or Cell Membrane Fragmentation.Biomacromolecules. 2023 Mar 13;24(3):1511-1521. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00028. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Biomacromolecules. 2023. PMID: 36802533 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer-Nanodiscs as a Novel Alignment Medium for High-Resolution NMR-Based Structural Studies of Nucleic Acids.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 3;12(11):1628. doi: 10.3390/biom12111628. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358983 Free PMC article.
-
Peptoid-based macrodiscs of variable lipid composition for structural studies of membrane proteins by oriented-sample solid-state NMR.J Struct Biol X. 2023 Dec 8;9:100095. doi: 10.1016/j.yjsbx.2023.100095. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Struct Biol X. 2023. PMID: 38094992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanders C.R., Schwonek J.P. Characterization of magnetically orientable bilayers in mixtures of DHPC and DMPC by solid state NMR. Biochemistry. 1992;31:8898–8905. - PubMed
-
- Vold R.R., Prosser R. Magnetically oriented phospholipid bilayered micelles for structural studies of polypeptides. Does the ideal bicelle exist? J. Magn. Reson. B. 1996;113:267–271.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

