Patients-associated compound etiology may have more severe acute pancreatitis: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 35919042
- PMCID: PMC9338379
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-21-1157
Patients-associated compound etiology may have more severe acute pancreatitis: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Currently, the concept of "a single cause results in acute pancreatitis (AP)" has been deeply incorporated into clinical practice, whereas the concept of "compound-etiology" has not attract considerable attention. This study aimed to explore the impact of the category of etiology on AP clinical outcomes.
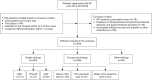
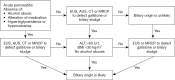
Methods: Patients with AP hospitalized within 72 h of symptom onset were retrospectively enrolled in this study from January 2014 to October 2019. AP etiology was classified into two main categories: single-etiology and compound-etiology category. The single-etiology category mainly includes biliary, hypertriglyceridemia (HTG), and alcohol. The compound-etiology category refers to AP with two or more causes, which mainly include dual-etiology and triple-etiology category, that is the biliary-HTG type, HTG-alcoholic type, and biliary-HTG-alcoholic type. The general information and clinical outcomes were reviewed and compared in AP patients with different etiologies.
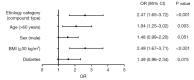
Results: Two hundred sixty-eight out of a total of 904 AP patients belonged to the compound-etiology category. Compared with the single-etiology category, the patients in the compound-etiology category were younger, more predominantly male, more likely to be obese (body mass index ≥30 kg/m2) and more likely to have pre-existing diabetes. The clinical outcomes were worse for patients with increasing complexity of etiology type, as shown by comparison of the incidence of any organ failure (P<0.001); persistent organ failure (POF) (P<0.001); intensive care unit need (P<0.001); local complications (P<0.001). AP with HTG had a higher rate of POF (P=0.032) and acute necrotic collection (P=0.013) than AP with biliary or alcohol involvement. When other etiologies simultaneously accompanied HTG-AP, the clinical outcomes were significantly worse than those in HTG-AP without other etiologies, particularly the biliary-HTG-alcoholic type. The compound-etiology category was independently associated with POF [odds ratio (OR): 2.47, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.65-3.72, P<0.001].
Conclusions: These results highlight the importance of determining AP etiology and the prevalence of the "compound-type" etiology. The compound-etiology category should be recognized as a separate concept in AP etiology and deserve higher priority.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis (AP); classification; diagnosis; etiology.
2022 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-21-1157/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG, Vege SS, Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group . Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013;62:102-11. 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
