Glycerol monolaurate attenuated immunological stress and intestinal mucosal injury by regulating the gut microbiota and activating AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-challenged broilers
- PMID: 35919246
- PMCID: PMC9307562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aninu.2022.06.005
Glycerol monolaurate attenuated immunological stress and intestinal mucosal injury by regulating the gut microbiota and activating AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-challenged broilers
Abstract
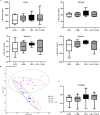
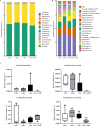
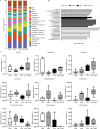
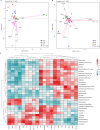
This study was conducted to investigate the effects of glycerol monolaurate (GML) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced immunological stress and intestinal mucosal injury in broilers and its underlying mechanisms. A total of 144 one-d-old Arbor Acres broilers were allocated to a 2 × 2 factorial arrangement involving dietary treatment (0 or 1,200 mg/kg dietary GML) and LPS challenge (injected with saline or Escherichia coli LPS on d 16, 18, and 20). Samples were collected on d 21. The results revealed that dietary GML augmented serum immunoglobulin A (P = 0.009) and immunoglobulin G (P < 0.001) levels in challenged birds. Dietary GML normalized LPS-induced variations in serum interleukin-6, interferon-gamma, and LPS levels (P < 0.05), jejunal villus height (P = 0.030), and gene expression of interleukin-6, macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha, Toll-like receptor 4, nuclear factor kappa-B, caspase-1, tight junction proteins, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase alpha 1 (AMPKα1), nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), and superoxide dismutase-1 (P < 0.05). GML supplementation ameliorated LPS-induced peroxidation by reducing malondialdehyde content and increasing antioxidant enzyme activity (P < 0.05). Dietary GML enhanced the abundances of Anaerostipes, Pseudoflavonifractor, and Gordonibacter and reduced the proportion of Phascolarctobacterium in challenged birds. Dietary GML was positively correlated with alterations in antioxidant enzyme activities and AMPKα1, Nrf2, and zonula occludens-1 expressions. The genera Anaerostipes, Lachnospira, Gordonibacter, Lachnospira, Marvinbryantia, Peptococcus, and Pseudoflavonifractor were linked to attenuated inflammation and improved antioxidant capacity of challenged birds. In conclusion, dietary GML alleviated LPS-induced immunological stress and intestinal injury of broilers by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress. Dietary GML regulated cecal microbiota and activated the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway in LPS-challenged broilers.
Keywords: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; Antioxidation; Glycerol monolaurate; Gut microbiota; Inflammation; Lipopolysaccharide challenge.
© 2022 Chinese Association of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co. Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, and there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the content of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycerol Monolaurate Ameliorated Intestinal Barrier and Immunity in Broilers by Regulating Intestinal Inflammation, Antioxidant Balance, and Intestinal Microbiota.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 23;12:713485. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.713485. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34630388 Free PMC article.
-
Glycerol monolaurate improves intestinal morphology and antioxidant status by suppressing inflammatory responses and nuclear factor kappa-B signaling in lipopolysaccharide-exposed chicken embryos.Anim Nutr. 2023 Sep 11;15:297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.06.014. eCollection 2023 Dec. Anim Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38033609 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary leonurine hydrochloride supplementation attenuates lipopolysaccharide challenge-induced intestinal inflammation and barrier dysfunction by inhibiting the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway in broilers.J Anim Sci. 2019 Apr 3;97(4):1679-1692. doi: 10.1093/jas/skz078. J Anim Sci. 2019. PMID: 30789669 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary resveratrol supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, intestinal immunity and gut microbiota in yellow-feathered broilers challenged with lipopolysaccharide.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 25;13:977087. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.977087. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36090096 Free PMC article.
-
Artemisia ordosica Polysaccharide Alleviated Lipopolysaccharide-induced Oxidative Stress of Broilers via Nrf2/Keap1 and TLR4/NF-κB Pathway.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Oct 15;223:112566. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112566. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 34340153
Cited by
-
Zinc Laurate Protects against Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction and Inflammation Induced by ETEC in a Mice Model.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 22;15(1):54. doi: 10.3390/nu15010054. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36615713 Free PMC article.
-
Carvacrol attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal injury by down-regulating TLRs gene expression and regulating the gut microbiota in rabbit.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 15;13(1):11447. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38577-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37454126 Free PMC article.
-
Inclusion of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei NSMJ15 in broiler diets induces changes in jejunal immune cell population and cecal microbiota.Anim Biosci. 2024 Dec;37(12):2155-2166. doi: 10.5713/ab.24.0162. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Anim Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38938030 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Hydroxytyrosol Supplementation on Growth Performance, Gut Morphometry, and Oxidative and Inflammatory Status in LPS-Challenged Broilers.Animals (Basel). 2024 Mar 12;14(6):871. doi: 10.3390/ani14060871. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539969 Free PMC article.
-
Methionine Alters the Fecal Microbiota and Enhances the Antioxidant Capacity of Lactating Donkeys.Animals (Basel). 2025 Feb 23;15(5):648. doi: 10.3390/ani15050648. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amer S.A., A-Nasser A., Al-Khalaifah H.S., AlSadek D.M.M., Abdel fattah D.M., Roushdy E.M., et al. Effect of dietary medium-chain α-monoglycerides on the growth performance, intestinal histomorphology, amino acid digestibility, and broiler chickens' blood biochemical parameters. Animals. 2021;11:57. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angelakis E. Weight gain by gut microbiota manipulation in productive animals. Microb Pathog. 2017;106:162–170. - PubMed
-
- Burlikowska K. Dietary fructans and their potential beneficial influence on health and performance parametres in broiler chickens. J Cent Eur Agric. 2012;13:272.
-
- Byun E.B., Sung N.Y., Byun E.H., Song D.S., Kim J.K., Park J.H., et al. The procyanidin trimer C1 inhibits LPS-induced MAPK and NF-κB signaling through TLR4 in macrophages. Int Immunopharm. 2013;15:450–456. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

