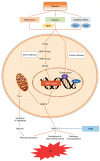
Molecules related to diabetic retinopathy in the vitreous and involved pathways
- PMID: 35919310
- PMCID: PMC9318090
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2022.07.20
Molecules related to diabetic retinopathy in the vitreous and involved pathways
Abstract
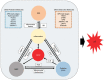
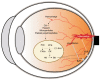
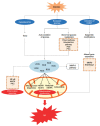
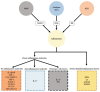
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is one of the most common complications of diabetes and major cause of blindness among people over 50 years old. Current studies showed that the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) played a central role in the pathogenesis of DR, and application of anti-VEGF has been widely acknowledged in treatment of DR targeting retinal neovascularization. However, anti-VEGF therapy has several limitations such as drug resistance. It is essential to develop new drugs for future clinical practice. The vitreous takes up 80% of the whole globe volume and is in direct contact with the retina, making it possible to explore the pathogenesis of DR by studying related factors in the vitreous. This article reviewed recent studies on DR-related factors in the vitreous, elaborating the VEGF upstream hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) pathway and downstream pathways phosphatidylinositol diphosphate (PIP2), phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K), and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. Moreover, factors other than VEGF contributing to the pathogenesis of DR in the vitreous were also summarized, which included factors in four major systems, kallikrein-kinin system such as bradykinin, plasma kallikrein, and coagulation factor XII, oxidative stress system such as lipid peroxide, and superoxide dismutase, inflammation-related factors such as interleukin-1β/6/13/37, and interferon-γ, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) system such as MMP-9/14. Additionally, we also introduced other DR-related factors such as adiponectin, certain specific amino acids, non-coding RNA and renin (pro) receptor in separate studies.
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy; molecular pathway; vascular endothelial growth factor; vitreous.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures

References
-
- Simó-Servat O, Hernández C, Simó R. Diabetic retinopathy in the context of patients with diabetes. Ophthalmic Res. 2019;62(4):211–217. - PubMed
-
- Wong TY, Cheung CMG, Larsen M, Sharma S, Simó R. Diabetic retinopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16012. - PubMed
-
- Liu R, Liu CM, Cui LL, Zhou L, Li N, Wei XD. Expression and significance of MiR-126 and VEGF in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(15):6387–6393. - PubMed
-
- Grauslund J. Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition for proliferative diabetic retinopathy: Et Tu, Brute? Acta Ophthalmol. 2017;95(8):757–758. - PubMed
-
- Loukovaara S, Nurkkala H, Tamene F, Gucciardo E, Liu XN, Repo P, Lehti K, Varjosalo M. Quantitative proteomics analysis of vitreous humor from diabetic retinopathy patients. J Proteome Res. 2015;14(12):5131–5143. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
