Visual acuity of urban and rural adults in a coastal province of southern China: the Fujian Eye Study
- PMID: 35919332
- PMCID: PMC9318102
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2022.07.17
Visual acuity of urban and rural adults in a coastal province of southern China: the Fujian Eye Study
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the vision status and sociodemographic associations of visual acuity (VA) in an urban and rural population in a coastal province of southern China.
Methods: The Fujian Eye Study, a population-based cross-sectional study, was performed from May 2018 to October 2019. Totally 10 044 participants over 50 years old from all nine cities in Fujian Province were enrolled, and underwent a questionnaire and a series of standard physical and ocular examinations. VA was measured by E Standard Logarithmic Visual Acuity Chart (GB 11533-1989). Data was double entered with EpiData v3.1 for data collation and Stata/SE statistical software v15.1 was used to analyze the data.
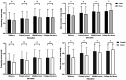
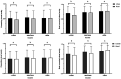
Results: Totally 8211 (81.8%) participants were finally included and were divided into urban populations (4678 subjects), rural populations (n=3533), coastal residents (n=6434), and inland residents (1777 subjects); 4836 participants were female. The mean age was 64.39±8.87y (median 64y; range 50-98y). The mean presenting VA was 0.61±0.30 (0.23±0.27 logMAR), and the mean best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 0.82±0.28 (0.08±0.19 logMAR). In the multiple regression analysis, BCVA was significantly correlated with several socioeconomic and biologic factors, including age (P<0.001), education level (P<0.001), income (P=0.005), rural residency (P<0.001), inland residency (P=0.001) and refractive error (P<0.001), while sex (P=0.194) was independent with BCVA.
Conclusion: Accessible services and eye health policies targeting the elderly, people with high myopia and people living in rural or inland areas are needed.
Keywords: best corrected visual acuity; coastal and inland; cross sectional eye study; presenting visual acuity; urban and rural.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Fujian eye cross sectional study: objectives, design, and general characteristics.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Mar 11;22(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02346-6. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35277140 Free PMC article.
-
Intraocular pressure of adults in a coastal province in southern China: the Fujian cross-sectional eye study.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Dec;10(12):12390-12402. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3238. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 35016405
-
Uncorrected near vision acuity and associated factors in a coastal province in southern China: the Fujian eye cross sectional study.Ann Transl Med. 2022 May;10(10):565. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1526. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35722396 Free PMC article.
-
Visual acuity in northern China in an urban and rural population: the Beijing Eye Study.Br J Ophthalmol. 2005 Sep;89(9):1089-93. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.068429. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 16113354 Free PMC article.
-
Refractive error in urban and rural adult Chinese in Beijing.Ophthalmology. 2005 Oct;112(10):1676-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.05.015. Ophthalmology. 2005. PMID: 16111755
Cited by
-
Hyperlipidemia and apolipoprotein E are associated with intraocular pressure of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy in a Chinese population: a cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 28;15:1484343. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1484343. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39669501 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence and causes of visual impairment in special schools and blind schools in Shanxi Province, China: a cross-sectional study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 11;15(1):25028. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07364-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40646013 Free PMC article.
-
The Australian Eye and Ear Health Survey (AEEHS): Study protocol for a population-based cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2024 May 31;19(5):e0301846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301846. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38820367 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in incidence and mortality for gynaecological cancers in Southeastern China during 2011-2020: a retrospective analysis of registry data.BMJ Open. 2024 Sep 28;14(9):e083336. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-083336. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39343456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourne RRA, Flaxman SR, Braithwaite T, et al. Magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5(9):e888–e897. - PubMed
-
- Liang YB, Friedman DS, Wong TY, et al. Rationale, design, methodology, and baseline data of a population-based study in rural China: the Handan Eye Study. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2009;16(2):115–127. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
