Statin-Induced Rhabdomyolysis Associated With Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement
- PMID: 35919670
- PMCID: PMC9287266
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000774
Statin-Induced Rhabdomyolysis Associated With Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement
Abstract
Rhabdomyolysis is a known rare and potentially lethal complication of statin use. This toxic effect is potentiated by alterations in hepatic physiology in patients with cirrhosis. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement has the potential to further compound this effect; yet, examples of this have not previously been described in the literature. We present a case of a patient who experienced statin-induced rhabdomyolysis likely as a direct consequence of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
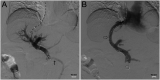

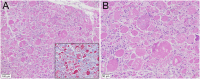
References
-
- Rodríguez-Laiz JM, Bańares R, Echenagusia A, et al. Effects of transjugular intrahepatic portasystemic shunt (TIPS) on splanchnic and systemic hemodynamics, and hepatic function in patients with portal hypertension. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:2121–7. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Gorski JC, Patel NH, et al. Hepatic and intestinal cytochrome P450 3A activity in cirrhosis: Effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology. 2001;34:1103–8. - PubMed
-
- Bassell T, Aminlari A, Hayden S, et al. Phenytoin toxicity after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS). J Emerg Med. 2021;60:54–7.e1. - PubMed
-
- Spriet I, Meyfroidt G, Maleux G, et al. The impact of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on the pharmacokinetics of caspofungin in a critically ill patient. Pharmacology. 2012;90:247–50. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

