Solution structure of a thrombin binding aptamer complex with a non-planar platinum(ii) compound
- PMID: 35919711
- PMCID: PMC9297526
- DOI: 10.1039/d2sc01196d
Solution structure of a thrombin binding aptamer complex with a non-planar platinum(ii) compound
Abstract
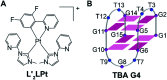
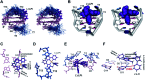
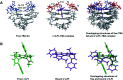
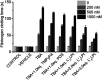
Thrombin Binding Aptamer (TBA) is a monomolecular well-defined two G-tetrad antiparallel G-quadruplex DNA that inhibits the activity of human α-thrombin. In this report, we synthesized a quasi-cross-shaped platinum(ii) compound (L'2LPt) with one cyclometalated and two carbene ligands. We found L'2LPt has selective affinity to bind the TBA G-quadruplex. A fibrinogen clotting assay revealed that L'2LPt can abrogate the inhibitory activity of TBA against thrombin. We solved the 1 : 1 L'2LPt-TBA complex structure by NMR, which revealed a unique self-adaptive property of L'2LPt upon binding to TBA. In the complex, a carbene ligand of L'2LPt rotates to pair with the cyclometalated ligand to form a plane stacking over half of the TBA G-tetrad and covered by lateral TT loops. It is notable that the heavy atom Pt stays out of the G-tetrad. Meanwhile, the other carbene ligand remains relatively perpendicular and forms a hydrogen bond with a guanine to anchor the L'2LPt position. This structure exhibits a quasi-cross-shaped Pt(ii) compound bound to the G-quadruplex with an unusual "wall-mounted" binding mode. Our structures provide insights into the specific recognition of antiparallel G-quadruplex DNA by a self-adaptive Pt(ii) compound and useful information for the design of selective G-quadruplex targeting non-planar molecules.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cation Coordination Alters the Conformation of a Thrombin-Binding G-Quadruplex DNA Aptamer That Affects Inhibition of Thrombin.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016 Oct;26(5):299-308. doi: 10.1089/nat.2016.0606. Epub 2016 May 9. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016. PMID: 27159247
-
Improving the Biological Properties of Thrombin-Binding Aptamer by Incorporation of 8-Bromo-2'-Deoxyguanosine and 2'-Substituted RNA Analogues.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 24;24(21):15529. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115529. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958511 Free PMC article.
-
Raman Scattering Reveals Ion-Dependent G-Quadruplex Formation in the 15-mer Thrombin-Binding Aptamer upon Association with α-Thrombin.Anal Chem. 2023 Nov 7;95(44):16160-16168. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02751. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37870982
-
Thrombin binding aptamer, more than a simple aptamer: chemically modified derivatives and biomedical applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(14):2036-47. doi: 10.2174/138161212799958387. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22376107 Review.
-
G-quadruplex-based aptamers targeting human thrombin: Discovery, chemical modifications and antithrombotic effects.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jan;217:107649. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107649. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 32777331 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of G-quadruplex targets in gastrointestinal cancers: Advancements, challenges and prospects.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Jul 15;15(7):1149-1173. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i7.1149. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37546556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solution structures and effects of a platinum compound successively bound MYC G-quadruplex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Sep 9;52(16):9397-9406. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae649. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39077944 Free PMC article.
-
Unmodified RNA sequences form unusual stable G-quadruplexes with potential anti-RSV and anti-angiogenesis applications.Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 21;8(1):474. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07915-1. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40119117 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Chirality on the β-Amino-Acid Naphthalenediimides/G-Quadruplex DNA Interaction.Molecules. 2023 Oct 27;28(21):7291. doi: 10.3390/molecules28217291. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37959711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stefan L. Monchaud D. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019;3:650–668. doi: 10.1038/s41570-019-0132-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

