Potential human immunotherapeutics for plague
- PMID: 35919741
- PMCID: PMC9327098
- DOI: 10.1093/immadv/ltab020
Potential human immunotherapeutics for plague
Abstract
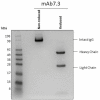
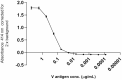
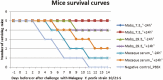
Two monoclonal antibodies directed to the V antigen of Yersinia pestis have been tested for protective efficacy in a murine model of bubonic plague. Mice were infected with a current clinical isolate from Madagascar, designated Y. pestis 10-21/S. Mab7.3, delivered to mice intra-periteoneally at either 24 h prior to, or 24 h post-infection, was fully protective, building on many studies which have demonstrated the protective efficacy of this Mab against a number of different clinical isolates of Y. pestis. Mab 29.3, delivered intra-peritoneally at either -24 h or +24 h, protected 4/5 mice in either condition; this has demonstrated the protective efficacy of this Mab in vivo for the first time. These results add to the cumulative data about Mab7.3, which is currently being humanized and highlight its potential as a human immunotherapeutic for plague, which is an enduring endemic disease in Madagascar and other regions of Africa, Asia, and South America.
Keywords: Plague; clinical isolate; immunotherapeutic; passive therapy; protection.
© Crown copyright 2021.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Plague around the world, 2010–2015. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2016;91(8):89–93. http://www.who.int/wer - PubMed
-
- Plague outbreak in Madagascar; external situation report 14, 4 Dec 2017, WHO; afro.who.int/health-topics/plague/plague-outbreak-situation-reports.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
