Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging improves prognostic stratification of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction and preserved ejection fraction
- PMID: 35919884
- PMCID: PMC9263884
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjopen/oeab033
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging improves prognostic stratification of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction and preserved ejection fraction
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the prognostic validity of clinical risk factors as well as infarct characterization and myocardial deformation by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) in ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) following primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
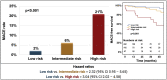
Methods and results: This multicentre, individual patient-data analysis from two large CMR trials included 1247 STEMI patients. Cardiac magnetic resonance examinations were conducted 3 [interquartile range (IQR) 2-4] days after PCI. LVEF, infarct size, microvascular obstruction (MVO), and myocardial strain values were measured. Primary endpoint was defined as composite of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) including death, re-infarction, and congestive heart failure. A preserved LVEF (defined as LVEF ≥50%) was observed in 724 patients (=58%). In the overall cohort, 97 patients experienced a MACE event [follow-up time 12 (IQR 12-13) months], and 34 MACE events occurred in the group with preserved LVEF (5% vs. 12% incidence rate in patients with LVEF < 50%). TIMI risk score [hazard ratio (HR) 1.28, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.02-1.59; P = 0.03] and female gender (HR 2.24, 95% CI 1.10-4.57; P = 0.03) emerged as independent clinical determinants of MACE in the patient group with preserved LVEF. Among CMR parameters, the presence of MVO (HR 2.39, 95% CI 1.05-5.46; P = 0.04) and reduced global longitudinal strain (GLS; HR 1.12, 95% CI 1.02-1.23; P = 0.02) independently predicted MACE in the LVEF-preserved population. The addition of MVO and GLS to the clinical prognostic markers (TIMI risk score, female gender) increased (P = 0.02) the prognostic validity [AUC 0.76 (95% CI 0.73-0.79)] compared to the clinical markers alone [AUC 0.65 (0.62-0.69)].
Conclusion: In contemporary treated STEMI patients showing preserved LVEF, a CMR-based risk prediction approach assessing MVO and GLS provided strong prognostic value that was incremental to clinical outcome parameters.
Keywords: Cardiac magnetic resonance; Preserved ejection fraction; ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microvascular obstruction extent predicts major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute myocardial infarction and preserved ejection fraction.Eur Radiol. 2019 May;29(5):2369-2377. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5895-z. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30552479
-
Prognostic Implications of Global Longitudinal Strain by Feature-Tracking Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Nov;12(11):e009404. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009404. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31679391
-
Global longitudinal strain improves risk assessment after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a comparative prognostic evaluation of left ventricular functional parameters.Clin Res Cardiol. 2021 Oct;110(10):1599-1611. doi: 10.1007/s00392-021-01855-6. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Clin Res Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33884479 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of myocardial salvage index by cardiac magnetic resonance in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2023 Nov;33(11):8214-8225. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09739-1. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37328640
-
The REFLO-STEMI (REperfusion Facilitated by LOcal adjunctive therapy in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction) trial: a randomised controlled trial comparing intracoronary administration of adenosine or sodium nitroprusside with control for attenuation of microvascular obstruction during primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2016 Dec. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2016 Dec. PMID: 27929619 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging-derived intraventricular pressure gradients in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a long-term follow-up study.Eur Heart J Imaging Methods Pract. 2024 Feb 9;2(1):qyae009. doi: 10.1093/ehjimp/qyae009. eCollection 2024 Jan. Eur Heart J Imaging Methods Pract. 2024. PMID: 39045208 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Microvascular Obstruction and Intra-Myocardial Hemorrhage in Reperfusion Cardiac Injury. Analysis of Clinical Data.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Mar 14;25(3):105. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2503105. eCollection 2024 Mar. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39076959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prognostic value of global longitudinal strain in patients with myocardial infarction and preserved ejection fraction: a prespecified substudy of the REDUCE-AMI trial.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025 Mar 27;26(4):620-627. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeaf015. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39813147 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey DE, Chung MK, de Lemos JA, Ettinger SM, Fang JC, Fesmire FM, Franklin BA, Granger CB, Krumholz HM, Linderbaum JA, Morrow DA, Newby LK, Ornato JP, Ou N, Radford MJ, Tamis-Holland JE, Tommaso CL, Tracy CM, Woo YJ, Zhao DX.. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;61:e78–e140. - PubMed
-
- Cikes M, Solomon SD.. Beyond ejection fraction: an integrative approach for assessment of cardiac structure and function in heart failure. Eur Heart J 2016;37:1642–1650. - PubMed
-
- Hanania G, Cambou JP, Gueret P, Vaur L, Blanchard D, Lablanche JM. et al. Management and in-hospital outcome of patients with acute myocardial infarction admitted to intensive care units at the turn of the century: results from the French nationwide USIC 2000 registry. Heart 2004;90:1404–1410. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ng VG, Lansky AJ, Meller S, Witzenbichler B, Guagliumi G, Peruga JZ, Brodie B, Shah R, Mehran R, Stone GW.. The prognostic importance of left ventricular function in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: the HORIZONS-AMI trial. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care 2014;3:67–77. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

