Plasmodium berghei leucine-rich repeat protein 1 downregulates protein phosphatase 1 activity and is required for efficient oocyst development
- PMID: 35920043
- PMCID: PMC9346556
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.220015
Plasmodium berghei leucine-rich repeat protein 1 downregulates protein phosphatase 1 activity and is required for efficient oocyst development
Abstract
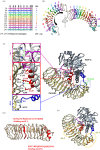
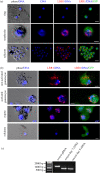
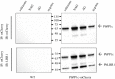
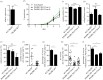
Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) is a key enzyme for Plasmodium development. However, the detailed mechanisms underlying its regulation remain to be deciphered. Here, we report the functional characterization of the Plasmodium berghei leucine-rich repeat protein 1 (PbLRR1), an orthologue of SDS22, one of the most ancient and conserved PP1 interactors. Our study shows that PbLRR1 is expressed during intra-erythrocytic development of the parasite, and up to the zygote stage in mosquitoes. PbLRR1 can be found in complex with PbPP1 in both asexual and sexual stages and inhibits its phosphatase activity. Genetic analysis demonstrates that PbLRR1 depletion adversely affects the development of oocysts. PbLRR1 interactome analysis associated with phospho-proteomics studies identifies several novel putative PbLRR1/PbPP1 partners. Some of these partners have previously been characterized as essential for the parasite sexual development. Interestingly, and for the first time, Inhibitor 3 (I3), a well-known and direct interactant of Plasmodium PP1, was found to be drastically hypophosphorylated in PbLRR1-depleted parasites. These data, along with the detection of I3 with PP1 in the LRR1 interactome, strongly suggest that the phosphorylation status of PbI3 is under the control of the PP1-LRR1 complex and could contribute (in)directly to oocyst development. This study provides new insights into previously unrecognized PbPP1 fine regulation of Plasmodium oocyst development through its interaction with PbLRR1.
Keywords: PP1; SDS22; inhibitor 3; leucine-rich repeat protein 1; protein phosphatase 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Essential role of GEXP15, a specific Protein Phosphatase type 1 partner, in Plasmodium berghei in asexual erythrocytic proliferation and transmission.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jul 26;15(7):e1007973. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007973. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31348803 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping PP1c and Its Inhibitor 2 Interactomes Reveals Conserved and Specific Networks in Asexual and Sexual Stages of Plasmodium.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 19;23(3):1069. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031069. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35162991 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatase 1: life-course regulation by SDS22 and Inhibitor-3.FEBS J. 2022 Jun;289(11):3072-3085. doi: 10.1111/febs.16029. Epub 2021 Jun 13. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34028981 Review.
-
A complex of catalytically inactive protein phosphatase-1 sandwiched between Sds22 and inhibitor-3.Biochemistry. 2007 Aug 7;46(31):8909-19. doi: 10.1021/bi7003119. Epub 2007 Jul 14. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17630778
-
Structure-Guided Exploration of SDS22 Interactions with Protein Phosphatase PP1 and the Splicing Factor BCLAF1.Structure. 2019 Mar 5;27(3):507-518.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2018.12.002. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Structure. 2019. PMID: 30661852 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Among-population proteomic differences in Schistocephalus solidus based on excretory/secretory and total body protein predictions.Parasit Vectors. 2025 May 20;18(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s13071-025-06807-x. Parasit Vectors. 2025. PMID: 40394694 Free PMC article.
-
PP1 phosphatase controls both daughter cell formation and amylopectin levels in Toxoplasma gondii.PLoS Biol. 2024 Sep 10;22(9):e3002791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002791. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39255306 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

