Aromatic disulfides as potential inhibitors against interaction between deaminase APOBEC3G and HIV infectivity factor
- PMID: 35920198
- PMCID: PMC9828099
- DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2022049
Aromatic disulfides as potential inhibitors against interaction between deaminase APOBEC3G and HIV infectivity factor
Abstract
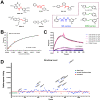
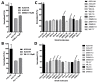
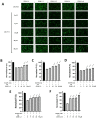
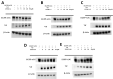
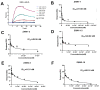
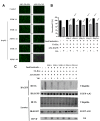
APOBEC3G (A3G) is a member of cytosine deaminase family with a variety of innate immune functions. It displays activities against retrovirus and retrotransposon by inhibition of virus infectivity factor (Vif)-deficient HIV-1 replication. The interaction between A3G N-terminal domain and Vif directs the cellular Cullin 5 E3-ubiquitin ligase complex to ubiquitinate A3G, and leads to A3G proteasomal degradation, which is a potential target for anti-HIV drug. Currently, there are very few reports about stable small molecules targeting the interaction between A3G and Vif. In this study, we screened two series of small molecules containing carbamyl sulfamide bond or disulfide bond as bridges of two different aromatic rings. Five asymmetrical disulfides were successfully identified against interaction between A3G and Vif with the IC 50 values close to or smaller than 1 μM, especially, not through covalently binding with A3G or Vif. They restore the A3G expression in the presence of Vif by inhibiting Vif-induced A3G ubiquitination and degradation. This study opens a way to the discovery of new anti-HIV drugs.
Keywords: APOBEC3G; HIV-1; Vif; aromatic disulfide; interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV-1 Vif-mediated ubiquitination/degradation of APOBEC3G involves four critical lysine residues in its C-terminal domain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 17;106(46):19539-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906652106. Epub 2009 Nov 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19887642 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3G is degraded by the proteasomal pathway in a Vif-dependent manner without being polyubiquitylated.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 9;283(19):13124-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708728200. Epub 2008 Mar 6. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18326044 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel HIV-1 inhibitor targeting Vif-dependent degradation of human APOBEC3G protein.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 17;290(16):10504-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.626903. Epub 2015 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25724652 Free PMC article.
-
Various strategies for developing APOBEC3G protectors to circumvent human immunodeficiency virus type 1.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Mar 15;250:115188. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115188. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36773550 Review.
-
Vif and Apobec3G in the innate immune response to HIV: a tale of two proteins.Future Microbiol. 2008 Apr;3(2):145-54. doi: 10.2217/17460913.3.2.145. Future Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18366335 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral factors and their counteraction by HIV-1: many uncovered and more to be discovered.J Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Jul 29;16(2):mjae005. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjae005. J Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38318650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the catalytically active APOBEC3G bound to a DNA oligonucleotide inhibitor reveals tetrahedral geometry of the transition state.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 19;13(1):7117. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34752-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36402773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miyakawa K, Matsunaga S, Kanou K, Matsuzawa A, Morishita R, Kudoh A, Shindo K, et al. ASK1 restores the antiviral activity of APOBEC3G by disrupting HIV-1 Vif-mediated counteraction. Nat Commun. . 2015;6:6945. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7945. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jin J, Yan X, Liu Y, Lan W, Wang C, Xu B, Cao C. Recent advances in the structural studies on cytosine deaminase APOBEC3 family members and their nucleic acid complexes. Acta Chim Sin. . 2019;77:1089. doi: 10.6023/A19080296. - DOI
-
- Wang Y, Kinlock BL, Shao Q, Turner TM, Liu B. HIV-1 Vif inhibits G to A hypermutations catalyzed by virus-encapsidated APOBEC3G to maintain HIV-1 infectivity. Retrovirology. . 2014;11:89. doi: 10.1186/s12977-014-0089-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Britan-Rosich E, Nowarski R, Kotler M. Multifaceted counter-APOBEC3G mechanisms employed by HIV-1 Vif. J Mol Biol. . 2011;410:1065–1076. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.03.058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

