Weight Gain and Lipid Profile Changes in Koreans with Human Immunodeficiency Virus undergoing Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor-Based Regimens
- PMID: 35920267
- PMCID: PMC9533166
- DOI: 10.3947/ic.2022.0063
Weight Gain and Lipid Profile Changes in Koreans with Human Immunodeficiency Virus undergoing Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor-Based Regimens
Abstract
Background: This study explored the relationship between integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI)-based anti-retroviral agents and weight gain over time, and the risk factors for weight gain in Korean people living with human immunodeficiency virus (PLWH).
Materials and methods: The study was conducted retrospectively in PLWHs 18 years of age or older who took one of three INSTI-based single-tablet regimens (STRs) (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine/elvitegravir/cobicistat [TDF/F/EVG/c], tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine/elvitegravir/cobicistat [TAF/F/EVG/c], and abacavir/lamivudine/dolutegravir [ABC/3TC/DTG]) for more than 2 years at three university-affiliated hospitals in South Korea from May 2014 to December 2020. Analysis was performed in the treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced groups, respectively.
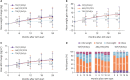
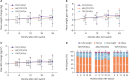
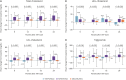
Results: Individual INSTI-based STRs were associated with weight gain at the 24-month follow up in both treatment-naïve (n = 179) and treatment-experienced (n = 290) groups. Body mass index (BMI) categories changed over time for TAF/F/EVG/c and ABC/3TC/DTG, with significant increases in the rates of overweight and obesity in treatment-naïve patients, whereas there was no change for TDF/F/EVG/c. TAF/F/EVG/c significantly increased total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and triglyceride (TG) compared to other regimens over 24 months. In the treatment-naïve group, a baseline CD4+ T cell count <100 cells/mm3, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) viral load (VL) ≥100,000 copies/mL, no physical exercise, and TAF/F/EVG/c (vs. TDF/F/EVF/c) were risk factors for ≥10% weight gain. In the treatment-experienced group, age <45 years, BMI <25 kg/m², and no physical exercise were risk factors for ≥5% weight gain.
Conclusion: INSTI-based STR continued to increase body weight at the 24-month follow up in treated and untreated Korean PLWH. Exercise, together with demographic-, HIV-, and anti-retroviral therapy-related factors, influenced weight gain. Therefore, when prescribing an INSTI-based STR, weight gain and metabolic changes should be closely monitored in PLWH with these risk factors.
Keywords: Anti-retroviral agents; Human immunodeficiency virus; Integrase inhibitor; Lipid; Weight gain.
Copyright © 2022 by The Korean Society of Infectious Diseases, Korean Society for Antimicrobial Therapy, and The Korean Society for AIDS.
Conflict of interest statement
SIJ is an associate editor of
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of switching to TAF/FTC/RPV, TAF/FTC/EVG/cobi and ABC/3TC/DTG on cardiovascular risk and lipid profile in people living with HIV: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Jun 22;21(1):595. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06304-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34157984 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Metabolic Effects of Three Different Treatment Combinations with Retrospective Real-life Data in People Living with HIV.Curr HIV Res. 2023;21(5):314-322. doi: 10.2174/011570162X266922231107094649. Curr HIV Res. 2023. PMID: 37990894
-
Renal profile of patients treated with elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide fumarate and dolutegravir/abacavir/lamivudine: 120-week results from a real-world cohort.Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2023 Jul;30(4):221-226. doi: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2021-002896. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2023. PMID: 34649965 Free PMC article.
-
Switching regimens in virologically suppressed HIV-1-infected patients: evidence base and rationale for integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI)-containing regimens.HIV Med. 2016 Oct;17 Suppl 5:3-16. doi: 10.1111/hiv.12440. HIV Med. 2016. PMID: 27714978 Review.
-
Strength in Amalgamation: Newer Combination Agents for HIV and Implications for Practice.Pharmacotherapy. 2018 Jan;38(1):86-107. doi: 10.1002/phar.2055. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Pharmacotherapy. 2018. PMID: 29105160 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk of dyslipidaemia in people living with HIV who are taking tenofovir alafenamide: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Int AIDS Soc. 2024 Sep;27(9):e26358. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26358. J Int AIDS Soc. 2024. PMID: 39301685 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dolutegravir-based first-line antiretroviral therapy on weight and body mass index among adult people living with HIV on follow up at health facilities in Hawassa city administration, Southern Ethiopia: a retrospective cohort study.Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2242250. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2242250. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 37531412 Free PMC article.
-
A Korean Post-Marketing Surveillance Study of Dolutegravir Single-Agent Tablets in Patients with HIV-1.Infect Chemother. 2022 Dec;54(4):711-721. doi: 10.3947/ic.2022.0058. Infect Chemother. 2022. PMID: 36596681 Free PMC article.
-
The Story and Implications of the Korean Health Care Facility Counseling Project on People Living with HIV.Infect Chemother. 2023 Jun;55(2):167-178. doi: 10.3947/ic.2023.0024. Epub 2023 May 18. Infect Chemother. 2023. PMID: 37272236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
12-week Dolutegravir treatment marginally reduces energy expenditure but does not increase body weight or alter vascular function in a murine model of Human Immunodeficiency Virus infection.Vascul Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;155:107288. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2024.107288. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Vascul Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38428626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents with HIV. Department of Health and Human Services; [Accessed 20 January 2022]. Available at https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/Ad....
-
- Ryom L, De Miguel R, Cotter AG, Podlekareva D, Beguelin C, Waalewijn H, Arribas JR, Mallon PWG, Marzolini C, Kirk O, Bamford A, Rauch A, Molina JM, Kowalska JD, Guaraldi G, Winston A, Boesecke C, Cinque P, Welch S, Collins S, Behrens GMN EACS Governing Board. Major revision version 11.0 of the European AIDS Clinical Society Guidelines 2021. HIV Med. 2022 [Epub ahead of print] - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

