Interventional Ultrasound in Dermatology: A Pictorial Overview Focusing on Cutaneous Melanoma Patients
- PMID: 35920315
- PMCID: PMC9805223
- DOI: 10.1002/jum.16073
Interventional Ultrasound in Dermatology: A Pictorial Overview Focusing on Cutaneous Melanoma Patients
Abstract
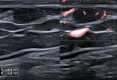
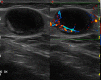
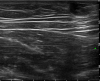
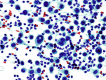
Cutaneous melanoma incidence is increasing worldwide, representing an aggressive tumor when evolving to the metastatic phase. High-resolution ultrasound (US) is playing a growing role in the assessment of newly diagnosed melanoma cases, in the locoregional staging prior to the sentinel lymph-node biopsy procedure, and in the melanoma patient follow-up. Additionally, US may guide a number of percutaneous procedures in the melanoma patients, encompassing diagnostic and therapeutic modalities. These include fine needle cytology, core biopsy, placement of presurgical guidewires, aspiration of lymphoceles and seromas, and electrochemotherapy.
Keywords: cutaneous melanoma; general ultrasound; intervention; nonvascular interventional radiology; oncologic imaging; ultrasound.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Validity of ultrasound-guided aspiration needle biopsy in the diagnosis of micrometastases in sentinel lymph nodes in patients with cutaneous melanoma.Vojnosanit Pregl. 2016 Oct;73(10):934-40. doi: 10.2298/VSP150227042S. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2016. PMID: 29328105
-
Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology prior to sentinel lymph node biopsy in melanoma patients.Ann Surg Oncol. 2006 Dec;13(12):1682-9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9046-4. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006. PMID: 17063307
-
Cutaneous melanoma: role of ultrasound in the assessment of locoregional spread.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2010 Jan-Feb;39(1):30-6. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2009.04.001. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2010. PMID: 19931111 Review.
-
Use of Lymph Node Ultrasound Prior to Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in 384 Patients with Melanoma: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis.Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017 Dec;108(10):931-938. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017. PMID: 28801012 English, Spanish.
-
Locoregional spread of cutaneous melanoma: sonography findings.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010 Mar;194(3):735-45. doi: 10.2214/AJR.09.2422. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010. PMID: 20173153 Review.
Cited by
-
Rationale for Using High-Frequency Ultrasound as a Routine Examination in Skin Cancer Surgery: A Practical Approach.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 8;13(7):2152. doi: 10.3390/jcm13072152. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38610917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-glandular findings on breast ultrasound. Part II: a pictorial review of chest wall lesions.J Ultrasound. 2023 Mar;26(1):49-58. doi: 10.1007/s40477-022-00773-1. Epub 2023 Jan 27. J Ultrasound. 2023. PMID: 36705852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound-guided percutaneous coil and thrombin embolization of a left gastric artery pseudoaneurysm.Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Sep 23;18(12):4281-4286. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.09.013. eCollection 2023 Dec. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37771379 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of pulmonary neoplasms: review of literature and future perspectives.Pol J Radiol. 2023 Apr 18;88:e216-e224. doi: 10.5114/pjr.2023.127062. eCollection 2023. Pol J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37234463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noninfectious Granulomatous Lung Disease: Radiological Findings and Differential Diagnosis.J Pers Med. 2024 Jan 23;14(2):134. doi: 10.3390/jpm14020134. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38392568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Corvino A, Corvino F, Catalano O, et al. The tail and the string sign: new sonographic features of subcutaneous melanoma metastasis. Ultrasound Med Biol 2017; 43:370–374. - PubMed
-
- Catalano O, Wortsman X. Dermatology ultrasound. Imaging technique, tips and tricks, high‐resolution anatomy. Ultrasound Q 2020; 36:321–327. - PubMed
-
- Uren RF, Sanki A, Thompson JF. The utility of ultrasound in patients with melanoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2007; 7:1633–1642. - PubMed
-
- Alfageme F, Wortsman X, Catalano O, et al. European Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology (EFSUMB) position statement on dermatologic ultrasound. Ultraschall Med 2021; 2:39–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

