Rice MPK17 Plays a Negative Role in the Xa21-Mediated Resistance Against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae
- PMID: 35920921
- PMCID: PMC9349333
- DOI: 10.1186/s12284-022-00590-4
Rice MPK17 Plays a Negative Role in the Xa21-Mediated Resistance Against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae
Abstract
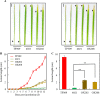
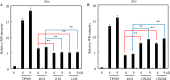
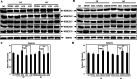
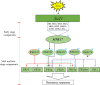
Rice bacterial blight, caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), is one of the most serious diseases affecting rice production worldwide. Xa21 was the first disease resistance gene cloned in rice, which encodes a receptor kinase and confers broad resistance against Xoo stains. Dozens of components in the Xa21-mediated pathway have been identified in the past decades, however, the involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) genes in the pathway has not been well described. To identify MAPK involved in Xa21-mediated resistance, the level of MAPK proteins was profiled using Western blot analysis. The abundance of OsMPK17 (MPK17) was found decreased during the rice-Xoo interaction in the background of Xa21. To investigate the function of MPK17, MPK17-RNAi and over-expression (OX) transgenic lines were generated. The RNAi lines showed an enhanced resistance, while OX lines had impaired resistance against Xoo, indicating that MPK17 plays negative role in Xa21-mediated resistance. Furthermore, the abundance of transcription factor WRKY62 and pathogenesis-related proteins PR1A were changed in the MPK17 transgenic lines when inoculated with Xoo. We also observed that the MPK17-RNAi and -OX rice plants showed altered agronomic traits, indicating that MPK17 also plays roles in the growth and development. On the basis of the current study and published results, we propose a "Xa21-MPK17-WRKY62-PR1A" signaling that functions in the Xa21-mediated disease resistance pathway. The identification of MPK17 advances our understanding of the mechanism underlying Xa21-mediated immunity, specifically in the mid- and late-stages.
Keywords: Bacterial blight; MAPK; Resistance gene Xa21; Rice; Transcription factor; WRKY.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Chen Q, Huang X, Chen X, Shamsunnaher SW. Reversible activation of XA21-mediated resistance by temperature. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2018;153:1177–1184. doi: 10.1007/s10658-018-01634-6. - DOI
-
- Chen R, Deng Y, Ding Y, Guo J, Qiu J, Wang B, Wang C, Xie Y, Zhang Z, Chen J, Chen L, Chu C, He G, He Z, Huang X, Xing Y, Yang S, Xie D, Liu Y, Li J (2021b) Rice functional genomics: decades’ efforts and roads ahead. Sci China Life Sci, 1–60 - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31400700/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31171528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- YJ201910/Introduced Talents of Hebei Agricultural University
- YJ201910/Introduced Talents of Hebei Agricultural University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

