A Nurse-Led mHealth Self-Management Program (mChemotherapy) for Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: Study Protocol of a Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
- PMID: 35921175
- PMCID: PMC9358201
- DOI: 10.1177/10732748221115469
A Nurse-Led mHealth Self-Management Program (mChemotherapy) for Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: Study Protocol of a Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
Abstract
Background: The global pandemic has caused breast cancer (BC) patients who are receiving chemotherapy to face more challenges in taking care of themselves than usual. A novel nurse-led mHealth program (mChemotherapy) is designed to foster self-management for this population. The aim of the pilot study is to determine the feasibility, usability, and acceptability of an mChemotherapy program for breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. The objective also is to evaluate the preliminary effects of this program on adherence to app usage, self-efficacy, quality of life, symptom burden, and healthcare utilization among this group of patients.
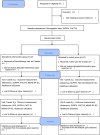
Methods: This is a single-blinded randomized controlled pilot study that includes one intervention group (mChemotherapy group) and one control group (routine care group). Ninety-four breast cancer patients who commence chemotherapy in a university-affiliated hospital will be recruited. Based on the Individual and Family Self-management Theory, this 6-week mChemotherapy program, which includes a combination of self-regulation activities and nurse-led support, will be provided. Data collection will be conducted at baseline, week 3 (T1), and week 6 (T2). A general linear model will be utilized for identifying the between-group, within-group, and interaction effects. Qualitative content analysis will be adopted to analyze, extract, and categorize the interview transcripts.
Discussions: Breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy are a population that often experiences a heavy symptom burden. During the pandemic, they have had difficulties in self-managing the side effects of chemotherapy due to the lack of face-to-face professional support. An mChemotherapy program will be adopted through a self-regulation process and with the provision of nurse-led real-time professional support for these patients. If proven effective, BC patients who engage in this program will be more likely to take an active role in managing their symptoms, take responsibility for their own health, and subsequently improve their self-efficacy and adherence to the use of the app.
Keywords: adjuvant chemotherapy; breast cancer; health care; management; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Feasibility of a mobile health app-based self-management program for Chinese patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy: A randomized controlled pilot study.Digit Health. 2024 Feb 25;10:20552076241231560. doi: 10.1177/20552076241231560. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38410790 Free PMC article.
-
Development and feasibility of an mHealth intervention for psychoeducational support of Nigerian women diagnosed with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy: A pilot randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 25;19(11):e0314365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314365. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39585879 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effects of Nurse-Led Supportive Care Program on Quality of Life in Women with Breast Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study.Semin Oncol Nurs. 2024 Apr;40(2):151609. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2024.151609. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38433074 Clinical Trial.
-
Mobile Health Application-Based Interventions to Improve Self-management of Chemotherapy-Related Symptoms Among People with Breast Cancer Who Are Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review.Oncologist. 2023 Apr 6;28(4):e175-e182. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyac267. Oncologist. 2023. PMID: 36801955 Free PMC article.
-
Telephone interventions for symptom management in adults with cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jun 2;6(6):CD007568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007568.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32483832 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Synergistic Effect of Nurse Proactive Phone Calls With an mHealth App Program on Sustaining App Usage: 3-Arm Randomized Controlled Trial.J Med Internet Res. 2023 May 1;25:e43678. doi: 10.2196/43678. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37126378 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Feasibility of a mobile health app-based self-management program for Chinese patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy: A randomized controlled pilot study.Digit Health. 2024 Feb 25;10:20552076241231560. doi: 10.1177/20552076241231560. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38410790 Free PMC article.
-
Oral self-management of palbociclib using mobile technology: Findings from a nurse-led randomized controlled trial.Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2024 Oct 15;11(12):100604. doi: 10.1016/j.apjon.2024.100604. eCollection 2024 Dec. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39697813 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical