Does aquatic physical therapy affect the rehabilitation of breast cancer in women? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 35921372
- PMCID: PMC9348687
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272337
Does aquatic physical therapy affect the rehabilitation of breast cancer in women? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
To determine and evaluate the benefits of aquatic physical therapy as a rehabilitation strategy for women with breast cancer on health outcomes. Electronic databases including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Weipu (VIP) and Wanfang database were systematically searched until June 2021. Randomized controlled trials were included if they evaluated the effects of aquatic physical therapy in breast cancer patients. The quality of the trials included was assessed by the two independent researchers according to the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook recommendations. Outcome measures were fatigue, waist circumference and quality of life (QoL). The study was registered under PROSPERO (CRD42021157323). Totally, five studies comprising 356 participants were included in the study. Meta-analyses showed that aquatic physical therapy interventions significantly reduced the fatigue score (MD = -2.14, 95%CI: -2.82, -1.45, p<0.01) compared with usual care; In addition, we also observed that, compared with land-based exercise, aquatic physical therapy greatly improved the QoL (MD = 2.85, 95%CI: 0.62, 5.09, p = 0.01). However, aquatic physical therapy cannot improve physical index (waist circumference) compared to usual care (MD = -3.49, 95%CI: -11.56,4.58, p = 0.4). Consequently, aquatic physical therapy had a positive effect on the fatigue and QoL. The results of this meta-analysis can provide a reliable evidence for evaluating the interventional effectiveness of aquatic physical therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
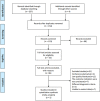
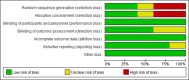
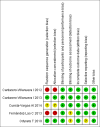


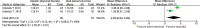
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

