Deacetylation of ATG4B promotes autophagy initiation under starvation
- PMID: 35921421
- PMCID: PMC9348796
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo0412
Deacetylation of ATG4B promotes autophagy initiation under starvation
Abstract
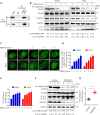
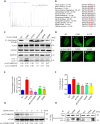
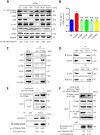
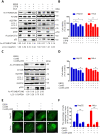
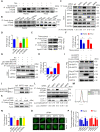
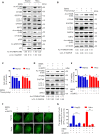
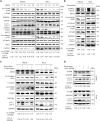
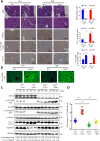
Eukaryotes initiate autophagy when facing environmental changes such as a lack of external nutrients. However, the mechanisms of autophagy initiation are still not fully elucidated. Here, we showed that deacetylation of ATG4B plays a key role in starvation-induced autophagy initiation. Specifically, we demonstrated that ATG4B is activated during starvation through deacetylation at K39 by the deacetylase SIRT2. Moreover, starvation triggers SIRT2 dephosphorylation and activation in a cyclin E/CDK2 suppression-dependent manner. Meanwhile, starvation down-regulates p300, leading to a decrease in ATG4B acetylation at K39. K39 deacetylation also enhances the interaction of ATG4B with pro-LC3, which promotes LC3-II formation. Furthermore, an in vivo experiment using Sirt2 knockout mice also confirmed that SIRT2-mediated ATG4B deacetylation at K39 promotes starvation-induced autophagy initiation. In summary, this study reveals an acetylation-dependent regulatory mechanism that controls the role of ATG4B in autophagy initiation in response to nutritional deficiency.
Figures
References
-
- Nakatogawa H., Mechanisms governing autophagosome biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 439–458 (2020). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

