Maxillary Midline Diastemas in West African Smiles
- PMID: 35922369
- PMCID: PMC10023582
- DOI: 10.1016/j.identj.2022.06.020
Maxillary Midline Diastemas in West African Smiles
Abstract
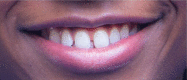
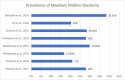
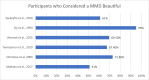
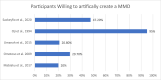
The maxillary midline diastema (MMD) has experienced a renaissance in popular culture over the last 10 years. Current literature states that MMDs should be eliminated where possible or be reduced to 1 mm or less in width. This literature review explores the evidence for this in a West African population. A systematic search of the literature (Medline and Google Scholar) followed by a hand search was carried out to identify all papers evaluating perceptions of MMDs. In all, 209 papers were identified in the literature search, 8 of which met the inclusion criteria. The review revealed that midline diastemas are desirable in this specific population with a width of 2 to 4 mm deemed as attractive. As many as 95% of participants found the MMD beautiful, and as many as 95% would consider having one created artificially. The literature does not support the position that MMDs larger than 1 mm should always be treated to be perceived as attractive in this population. MMDs are accepted as attractive and should be considered a key feature in smile design for this population.
Keywords: Attractiveness; Desirability; Gap tooth; Maxillary midline diastema; Perceptions; West Africa.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest None disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Attractiveness and determinants of maxillary midline diastemas in a West African smile.BDJ Open. 2025 Feb 18;11(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41405-025-00302-2. BDJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39966343 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of maxillary median diastema on the esthetics of a smile.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020 Oct;158(4):e37-e42. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2020.07.028. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020. PMID: 32988573
-
Prevalence of artificially created maxillary midline diastema and its complications in a selected nigerian population.Afr Health Sci. 2015 Mar;15(1):226-32. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v15i1.29. Afr Health Sci. 2015. PMID: 25834552 Free PMC article.
-
The midline diastema: a review of its etiology and treatment.Pediatr Dent. 1995 May-Jun;17(3):171-9. Pediatr Dent. 1995. PMID: 7617490 Review.
-
Midline diastema and its aetiology--a review.Dent Update. 2014 Jun;41(5):457-60, 462-4. doi: 10.12968/denu.2014.41.5.457. Dent Update. 2014. PMID: 25073229 Review.
Cited by
-
Smile Attractiveness and Treatment Needs of Maxillary Midline Diastema with Various Widths: Perception among Laypersons, Dental Students, and Dentists in Malaysia.Int J Dent. 2023 Apr 15;2023:9977868. doi: 10.1155/2023/9977868. eCollection 2023. Int J Dent. 2023. PMID: 37095900 Free PMC article.
-
Laypersons' perception of smile esthetics from different backgrounds.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2024 Jul 4;21:30. eCollection 2024. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2024. PMID: 39188396 Free PMC article.
-
Dental discrepancies in black adolescents: evaluating impacts on well-being.Braz Oral Res. 2025 Feb 7;39:e15. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2025.vol39.015. eCollection 2025. Braz Oral Res. 2025. PMID: 39936714 Free PMC article.
-
Attractiveness and determinants of maxillary midline diastemas in a West African smile.BDJ Open. 2025 Feb 18;11(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41405-025-00302-2. BDJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39966343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McVay TJ, Latta GH. Incidence of the maxillary midline diastema in adults. J Prosthet Dent. 1984;52(6):809–811. - PubMed
-
- Mabiaku YO, Ibawoh LO. Prevalence and perception of midline diastema amount Students of Instituts of Health Information Management of University of Benin Teach Hospital (UBTH) Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. Ng J Dent Res. 2017;2(1):33–36.
-
- Lavelle CLB. The distribution of diastemas in different human population samples. Eur J Oral Sci. 1970;78(1–4):530–534. - PubMed
-
- Newman-Nartey M, Sackeyfio J, Hewlett S, Amoah Nartey S, Otu-Nartey N. Prevalence, aetiology, management and retention of midline diastema in orthodontic patients in Ghana. West Afr J Orthod. 2016;5(1):16–22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

