A full year of turbulence measurements from a drift campaign in the Arctic Ocean 2019-2020
- PMID: 35922449
- PMCID: PMC9349312
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-022-01574-1
A full year of turbulence measurements from a drift campaign in the Arctic Ocean 2019-2020
Abstract
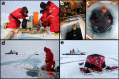
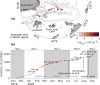
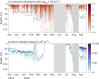
Ocean turbulent mixing is a key process in the global climate system, regulating ocean circulation and the uptake and redistribution of heat, carbon, nutrients, oxygen and other tracers. In polar oceans, turbulent heat transport additionally affects the sea ice mass balance. Due to the inaccessibility of polar regions, direct observations of turbulent mixing are sparse in the Arctic Ocean. During the year-long drift expedition "Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate" (MOSAiC) from September 2019 to September 2020, we obtained an unprecedented data set of vertical profiles of turbulent dissipation rate and water column properties, including oxygen concentration and fluorescence. Nearly 1,700 profiles, covering the upper ocean down to approximately 400 m, were collected in sets of 3 or more consecutive profiles every day, and complemented with several intensive sampling periods. This data set allows for the systematic assessment of upper ocean mixing in the Arctic, and the quantification of turbulent heat and nutrient fluxes, and can help to better constrain turbulence parameterizations in ocean circulation models.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Fer I. Weak vertical diffusion allows maintenance of cold halocline in the central Arctic. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters. 2009;2:148–152. doi: 10.1080/16742834.2009.11446789. - DOI
-
- Rippeth TP, et al. Tide-mediated warming of Arctic halocline by Atlantic heat fluxes over rough topography. Nature Geoscience. 2015;8:191. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2350. - DOI
-
- Polyakov IV, et al. Weakening of cold halocline layer exposes sea ice to oceanic heat in the eastern Arctic Ocean. Journal of Climate. 2020;33:8107–8123. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0976.1. - DOI
-
- Schulz K, et al. On the along-slope heat loss of the Boundary Current in the Eastern Arctic Ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. 2021;126:e2020JC016375. doi: 10.1029/2020JC016375. - DOI
-
- Rippeth, T. P. & Fine, E. C. Turbulent Mixing in a Changing Arctic Ocean. Oceanography10.5670/oceanog.2022.103 (2022).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

