Metabolomics insights into the interaction between Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and Epinephelus coioides
- PMID: 35922642
- PMCID: PMC9349296
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17387-6
Metabolomics insights into the interaction between Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and Epinephelus coioides
Abstract
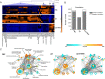
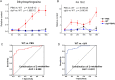
As a highly infectious epidemic in aquaculture, Pseudomonas plecoglossicida infection results in high mortality of teleosts and serious economic losses. Host-pathogen interactions shape the outcome of an infection, yet we still understand little about the molecular mechanism of these pathogen-mediated processes. Here, a P. plecoglossicida strain (NZBD9) and Epinephelus coioides were investigated as a model system to characterize pathogen-induced host metabolic remodeling over the course of infection. We present a non-targeted metabolomics profiling of E. coioides spleens from uninfected E. coioides and those infected with wild-type and clpV-RNA interference (RNAi) strains. The most significant changes of E. coioides upon infection were associated with amino acids, lysophospatidylcholines, and unsaturated fatty acids, involving disturbances in host nutritional utilization and immune responses. Dihydrosphingosine and fatty acid 16:2 were screened as potential biomarkers for assessing P. plecoglossicida infection. The silencing of the P. plecoglossicida clpV gene significantly recovered the lipid metabolism of infected E. coioides. This comprehensive metabolomics study provides novel insights into how P. plecoglossicida shape host metabolism to support their survival and replication and highlights the potential of the virulence gene clpV in the treatment of P. plecoglossicida infection in aquaculture.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dual RNA-Seq uncovers the function of an ABC transporter gene in the host-pathogen interaction between Epinephelus coioides and Pseudomonas plecoglossicida.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Sep;92:45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.05.046. Epub 2019 May 24. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31129188
-
The contributions of fliG gene to the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and pathogen-host interactions with Epinephelus coioides.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021 Dec;119:238-248. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2021.09.032. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34634455
-
flgC gene is involved in the virulence regulation of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and affects the immune response of Epinephelus coioides.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Jan;132:108512. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.108512. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36587883
-
Dual RNA-Seq Unveils Pseudomonas plecoglossicida htpG Gene Functions During Host-Pathogen Interactions With Epinephelus coioides.Front Immunol. 2019 May 3;10:984. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00984. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31130962 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of RNA-seq and RNAi reveals the contribution of znuA gene to the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and to the immune response of Epinephelus coioides.J Fish Dis. 2021 Nov;44(11):1831-1841. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13502. Epub 2021 Aug 2. J Fish Dis. 2021. PMID: 34339054
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

