Increased miR-124-3p alleviates type 2 inflammatory response in allergic rhinitis via IL-4Rα
- PMID: 35922673
- PMCID: PMC9616750
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-022-01614-x
Increased miR-124-3p alleviates type 2 inflammatory response in allergic rhinitis via IL-4Rα
Abstract
Background and objectives: miRNAs play a crucial role in regulating immune responses. However, the effect of miR-124-3p on type 2 inflammation in allergic rhinitis (AR) is unclear. We aimed to study the immune regulation of miR-124-3p in AR and the mechanisms involved.
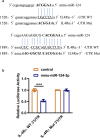
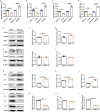
Methods: The direct interaction between miR-124-3p and IL-4Rα was confirmed through a dual-luciferase reporter assay. In vitro splenic lymphocytes from mice and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy individuals were cultured and treated with miR-124-3p mimic/inhibitor. Twenty-four female C57BL/C mice were divided into four groups: control, AR model, miR-124-3p agomir, and miR-124-3p antagomir groups (n = 6 per group). The allergic responses were evaluated based on the number of sneezing and nasal scratching, the serum HDM-specific IgE (sIgE) levels, and the degree of nasal mucosa eosinophil infiltration. The expression of IL-4Rα, p-STAT6, and type 2 inflammatory cytokines (IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13) in lymphocytes or nasal mucosa was determined by qPCR, western blotting, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence.
Results: miR-124-3p directly targets the 3'UTR of IL-4Rα. The miR-124-3p mimic lowered the IL-4Rα, p-STAT6, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 expression levels in both mouse splenic lymphocytes and human PBMCs in vitro, and the miR-124-3p inhibitor rescued these changes. Furthermore, the miR-124-3p agomir decreased the levels of IL-4Rα and IL-4 in nasal mucosa, Th2 differentiation in spleen, and allergic response in AR mice. Moreover, the miR-124-3p antagonist increased the IL-4Rα and IL-4 levels and further aggravated the allergic responses.
Conclusions: miR-124-3p might attenuate type 2 inflammation in AR by regulating IL-4Rα signaling, and miR-124-3p may be a promising new target in AR treatment.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; IL-4Rα; Inflammation; STAT6; miR-124-3p.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Settipane RA. Rhinitis: a dose of epidemiological reality. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2003;24:147–154. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

