Ursolic acid and SARS-CoV-2 infection: a new horizon and perspective
- PMID: 35922738
- PMCID: PMC9362167
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-022-01038-3
Ursolic acid and SARS-CoV-2 infection: a new horizon and perspective
Abstract
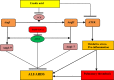
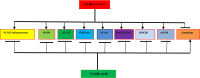
SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2) has been identified as the source of a world coronavirus pandemic in 2019. Covid-19 is considered a main respiratory disease-causing viral pneumonia and, in severe cases, leads to acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Although, extrapulmonary manifestations of Covid-19 like neurological, cardiovascular, and gastrointestinal have been confirmed. Exaggerated immune response and release of a high amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines may progress, causing a cytokine storm. Consequently, direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection can evolve into systemic complications due to the progression of hyper inflammation, oxidative stress and dysregulation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Therefore, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents could be efficient in alleviating these disorders. Ursolic acid has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiviral effects; it reduces the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, improves anti-inflammatory cytokines, and inhibits the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). In virtue of its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, ursolic acid may minimize SARS-CoV-2 infection-induced complications. Also, by regulating RAS and inflammatory signaling pathways, ursolic acid might effectively reduce the development of ALI in ARDS in Covid-19. In this state, this perspective discusses how ursolic acid can mitigate hyper inflammation and oxidative stress in Covid-19.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Antiviral; Covid-19; Immunity; Oxidative stress; Pandemics.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of berberine in Covid-19: potential adjunct therapy.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Dec;30(6):2003-2016. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01080-1. Epub 2022 Oct 2. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 36183284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitazoxanide and COVID-19: A review.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Nov;49(11):11169-11176. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07822-2. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36094778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A raising dawn of pentoxifylline in management of inflammatory disorders in Covid-19.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Jun;30(3):799-809. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00993-1. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35486310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Perspective on Erythropoietin as a Potential Adjuvant Therapy for Acute Lung Injury/Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Patients with COVID-19.Arch Med Res. 2020 Oct;51(7):631-635. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.08.002. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Arch Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32863034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of β-Blockers on the Sympathetic and Cytokines Storms in Covid-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 11;12:749291. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.749291. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34867978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ursolic acid: a natural modulator of signaling networks in different cancers.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Dec 10;22(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02804-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36496432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiology of Post-COVID syndromes: a new perspective.Virol J. 2022 Oct 9;19(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01891-2. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 36210445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection and dysregulation of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Nov;28(6):657-673. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01379-0. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 37796433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ursolic Acid Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting JAK2/STAT3-Driven Ferroptosis: Mechanistic Insights from Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Aug 4;19:6699-6717. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S526554. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40786248 Free PMC article.
-
Ursolic Acid Analogs as Potential Therapeutics for Cancer.Molecules. 2022 Dec 16;27(24):8981. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248981. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36558113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Kuraishy HM, Hussien NR, Al-Naimi MS, Al-Buhadily AK, Al-Gareeb AI, Lungnier C. Renin–angiotensin system and fibrinolytic pathway in COVID-19: one-way skepticism. Biomed Biotechnol Res J (BBRJ) 2020;4(5):33.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
