Oxalate-induced apoptosis through ERS-ROS-NF-κB signalling pathway in renal tubular epithelial cell
- PMID: 35922749
- PMCID: PMC9347104
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-022-00494-5
Oxalate-induced apoptosis through ERS-ROS-NF-κB signalling pathway in renal tubular epithelial cell
Abstract
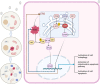
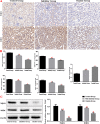
Background: Kidney stones are composed of approximately 70-80% calcium oxalate. However, the exact mechanism of formation of calcium oxalate kidney stones remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the NF-κB signalling pathway in the pathogenesis of oxalate-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury and its possible molecular mechanisms.
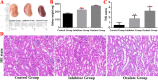
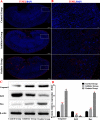
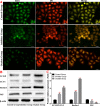
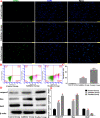
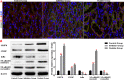
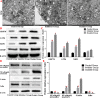
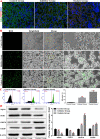
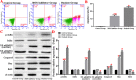
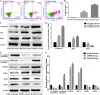
Methods: We established a model to evaluate the formation of kidney stones by intraperitoneal injection of glyoxylic acid solution into mice and assessed cell morphology, apoptosis, and the expression levels of ERS, ROS, and NF-κB signalling pathway-related proteins in mouse renal tissues. Next, we treated HK-2 cells with potassium oxalate to construct a renal tubular epithelial cell injury model. We detected the changes in autophagy, apoptosis, and mitochondrial membrane potential and investigated the ultrastructure of the cells by transmission electron microscopy. Western blotting revealed the expression levels of apoptosis and autophagy proteins; mitochondrial structural and functional proteins; and ERS, ROS, and NF-κB (p65) proteins. Lastly, we studied the downregulation of NF-κB activity in HK-2 cells by lentivirus interference and confirmed the interaction between the NF-κB signalling and ERS/ROS pathways.
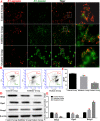
Results: We observed swelling of renal tissues, increased apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells, and activation of the ERS, ROS, and NF-κB signalling pathways in the oxalate group. We found that oxalate induced autophagy, apoptosis, and mitochondrial damage in HK-2 cells and activated the ERS/ROS/NF-κB pathways. Interestingly, when the NF-κB signalling pathway was inhibited, the ERS/ROS pathway was also inhibited.
Conclusion: Oxalate induces HK-2 cell injury through the interaction between the NF-κB signalling and ERS/ROS pathways.
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS); Kidney stones; NF-κB signalling pathway; Oxalate; Reactive oxygen species (ROS).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

