Evolutionary conserved relocation of chromatin remodeling complexes to the mitotic apparatus
- PMID: 35922843
- PMCID: PMC9351137
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-022-01365-5
Evolutionary conserved relocation of chromatin remodeling complexes to the mitotic apparatus
Abstract
Background: ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes are multi-protein machines highly conserved across eukaryotic genomes. They control sliding and displacing of the nucleosomes, modulating histone-DNA interactions and making nucleosomal DNA more accessible to specific binding proteins during replication, transcription, and DNA repair, which are processes involved in cell division. The SRCAP and p400/Tip60 chromatin remodeling complexes in humans and the related Drosophila Tip60 complex belong to the evolutionary conserved INO80 family, whose main function is promoting the exchange of canonical histone H2A with the histone variant H2A in different eukaryotic species. Some subunits of these complexes were additionally shown to relocate to the mitotic apparatus and proposed to play direct roles in cell division in human cells. However, whether this phenomenon reflects a more general function of remodeling complex components and its evolutionary conservation remains unexplored.
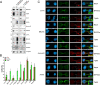
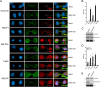
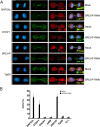
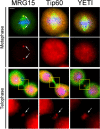
Results: We have combined cell biology, reverse genetics, and biochemical approaches to study the subcellular distribution of a number of subunits belonging to the SRCAP and p400/Tip60 complexes and assess their involvement during cell division progression in HeLa cells. Interestingly, beyond their canonical chromatin localization, the subunits under investigation accumulate at different sites of the mitotic apparatus (centrosomes, spindle, and midbody), with their depletion yielding an array of aberrant outcomes of mitosis and cytokinesis, thus causing genomic instability. Importantly, this behavior was conserved by the Drosophila melanogaster orthologs tested, despite the evolutionary divergence between fly and humans has been estimated at approximately 780 million years ago.
Conclusions: Overall, our results support the existence of evolutionarily conserved diverse roles of chromatin remodeling complexes, whereby subunits of the SRCAP and p400/Tip60 complexes relocate from the interphase chromatin to the mitotic apparatus, playing moonlighting functions required for proper execution of cell division.
Keywords: Cell division; Chromatin remodeling; Cytokinesis; Midbody; Moonlighting proteins.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Knockdown of DOM/Tip60 Complex Subunits Impairs Male Meiosis of Drosophila melanogaster.Cells. 2023 May 9;12(10):1348. doi: 10.3390/cells12101348. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408183 Free PMC article.
-
The ATPase SRCAP is associated with the mitotic apparatus, uncovering novel molecular aspects of Floating-Harbor syndrome.BMC Biol. 2021 Sep 2;19(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-01109-x. BMC Biol. 2021. PMID: 34474679 Free PMC article.
-
Unconventional roles of chromatin remodelers and long non-coding RNAs in cell division.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Nov 20;80(12):365. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04949-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37982870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila SWR1 and NuA4 complexes are defined by DOMINO isoforms.Elife. 2020 May 20;9:e56325. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56325. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32432549 Free PMC article.
-
The multitalented TIP60 chromatin remodeling complex: wearing many hats in epigenetic regulation, cell division and diseases.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2025 Jul 2;18(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13072-025-00603-8. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2025. PMID: 40604793 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-canonical role for the BAF complex subunit DPF3 in mitosis and ciliogenesis.J Cell Sci. 2024 May 1;137(9):jcs261744. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261744. Epub 2024 May 13. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 38661008 Free PMC article.
-
The Green Valley of Drosophila melanogaster Constitutive Heterochromatin: Protein-Coding Genes Involved in Cell Division Control.Cells. 2022 Sep 29;11(19):3058. doi: 10.3390/cells11193058. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tip60/KAT5 Histone Acetyltransferase Is Required for Maintenance and Neurogenesis of Embryonic Neural Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2113. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032113. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768434 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of memory assemblies through the DNA-sensing TLR9 pathway.Nature. 2024 Apr;628(8006):145-153. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07220-7. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38538785 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of DOM/Tip60 Complex Subunits Impairs Male Meiosis of Drosophila melanogaster.Cells. 2023 May 9;12(10):1348. doi: 10.3390/cells12101348. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flemming W. Zellsubstanz, Kern und Zelltheilung. 1882.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

