Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect retina in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa by anti-inflammation through miR-146a-Nr4a3 axis
- PMID: 35922863
- PMCID: PMC9351183
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-03100-x
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect retina in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa by anti-inflammation through miR-146a-Nr4a3 axis
Abstract
Background: Retinitis pigmentosa is a rod-cone degenerative disease that induces irreversible vision loss. This study probed the protective capacity of mesenchymal stem cell-derived small EVs (MSC-EVs) on the retinas of rd10 mice and the underlying mechanism.
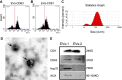
Methods: MSC-EVs were injected into the vitreous of rd10 mice at postnatal day 14 and P21; morphology and function were examined at P28. The mechanism of action was explored by using co-culture of photoreceptor cell line 661 W and microglia cell line BV2.
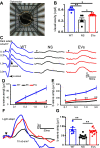
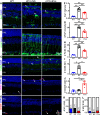
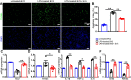
Results: Treatment with MSC-EVs increased the survival of photoreceptors and preserved their structure. Visual function, as reflected by optomotor and electroretinogram responses, was significantly enhanced in MSC-EVs-treated rd10 mice. Mechanistically, staining for Iba1, GFAP, F4/80, CD68 and CD206 showed that MSC-EVs suppressed the activation of microglial, Müller glial and macrophages. Furthermore, western blotting showed that the treatment inhibited the NF-κB pathway. RNA-seq and qPCR showed that MSC-EVs upregulated anti-inflammatory cytokines while downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines. MSC-EVs application in vitro decreased the number of TUNEL-positive 661 W cells co-cultured with LPS-stimulated BV2, with similar impact on the cytokine expression as in vivo study. Genetic screening predicted miR-146a to be the downstream target of MSC-EVs, which was detected in MSC-EVs and upregulated in co-cultured 661 W cells and BV2 cells after MSC-EVs treatment. Upregulation of miR-146a by using its mimic decreased the expression of the transcription factor Nr4a3, and its downregulation inhibition promoted Nr4a3 expression in both 661 W and BV2 cells. Nr4a3 was further identified as the target gene of miR-146a by dual-luciferase assay. Furthermore, overexpressing miR-146a significantly decreased the expression of LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines in BV2 cells.
Conclusions: MSC-EVs delays retinal degeneration in rd10 mice mainly by its anti-inflammatory effect via the miR-146a-Nr4a3axis. Hence, MSC-EVs may be used in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; Inflammation; Retinitis pigmentosa; miR-146a-Nr4a3 axis; rd10 mouse.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

