Toltrazuril and diclazuril: comparative evaluation of anti-coccidial drugs using a murine model
- PMID: 35922919
- PMCID: PMC9586018
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.22-0136
Toltrazuril and diclazuril: comparative evaluation of anti-coccidial drugs using a murine model
Abstract
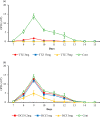
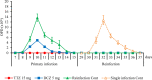
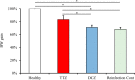
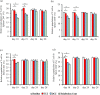
Intestinal coccidiosis caused by Eimeria protozoan species is an economically important disease, especially in poultry and cattle. Anti-coccidial drugs commonly used for controlling coccidiosis are toltrazuril (TTZ) and diclazuril (DCZ). In this study, the efficacies of TTZ and DCZ were compared using a murine model, and the effect of these treatments on the induction of acquired resistance was evaluated. Male C57BL/6J mice were inoculated with 1,000 sporulated E. vermiformis oocytes and treated with TTZ or DCZ. The recommended TTZ dose for cattle (15 mg/kg) completely prevented oocyte excretion. But, mice required 5 mg/kg of DCZ, which is five times the recommended dose for cattle, to reduce oocyte excretion. In E. vermiformis re-infection, TTZ (15 mg/kg) and DCZ (5 mg/kg) treatments did not interfere with the development of acquired resistance. Bodyweight gain was significantly higher in the TTZ-treated group than in the control (untreated/infected) group and the DCZ-treated group, and no significant difference in bodyweight gain was observed between the TTZ-treated group and the healthy (uninfected/untreated) group. Analysis of T lymphocyte subsets in the spleen and mesenteric lymph nodes indicated that the relative populations of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were reduced in the DCZ-treated and control (untreated/infected) groups, suggesting there was immunosuppression during the infection. However, no reductions in T cell populations were observed in the TTZ-treated group. The results indicated that an optimal anti-coccidial drug is one that can completely break the parasite life cycle in the host animal.
Keywords: Eimeria vermiformis; body-weight gain; diclazuril; host immunity; toltrazuril.
Figures
References
-
- Bohrmann R. 1991. Treatment with toltrazuril in a natural outbreak of coccidiosis in calves. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr 98: 343–345. - PubMed
-
- Daugschies A, Agneessens J, Goossens L, Mengel H, Veys P. 2007. The effect of a metaphylactic treatment with diclazuril (Vecoxan) on the oocyst excretion and growth performance of calves exposed to a natural Eimeria infection. Vet Parasitol 149: 199–206. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.08.003 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

