Determinants of Work-Related Stress Among Nurses Working in Private and Public Hospitals in Dessie City, 2021: Comparative Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 35923164
- PMCID: PMC9342705
- DOI: 10.2147/PRBM.S372882
Determinants of Work-Related Stress Among Nurses Working in Private and Public Hospitals in Dessie City, 2021: Comparative Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Globally, work-related stress had a significant impact on health-care providers. Private and public health-care institutions are considered intensive work areas for work-related stress. In Ethiopia, most studies were focused on only public hospitals. However, this study aimed to include private and public hospitals.
Methods: A hospital-based comparative cross-sectional study was conducted among 304 nurses working in public and private hospitals from 8 April to 7 May 2021. A simple random sampling technique was used to select nurses, and the data were collected using a standardized self-administered questionnaire. Data were entered into Epidata version 4.6.1 and then exported to SPSS version 26 for analysis. Descriptive statistics, bivariable and multivariable binary logistic regression were applied. The final multivariate regression declared significant determinants at a p-value <0.05 and a 95% confidence interval with an adjusted odds ratio (AOR) to reveal the strength of associated variables.
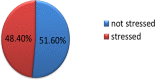
Results: In this study, the overall magnitude of work-related stress among nurses was 48.4% (95% CI: 42.4-54.6) (51.6% among public hospitals and 46.4% for private hospitals). Bachelor nurses (AOR=0.32,95% CI:0.13,0.76), working in operation room (AOR=7.89, 95% CI:1.46,9.60) and job dissatisfaction (AOR=4.95, 95% CI: 1.94,2.61) were determinants of work-stress in private hospitals whereas being female (AOR = 3.15, 95% CI: 1.43, 6.92), working experience 5 to 10 years (AOR=0.42, 95% CI: 0.18, 0.97), having degree and above (AOR = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.17, 0.99) and working in intensive care unit (AOR = 6.48, 95% CI:1.49, 8.18) were determinants of work-related stress in public hospitals.
Conclusion: The overall magnitude of work-related stress among nurses in Dessie city was almost half. In contrast, more work-related stress among nurses working in public hospitals than in private hospitals. Sex, operating (working) unit, working experience, and type of institution were work-related stress determinants in public and private hospitals. Hence, reducing workload and providing stress management training is crucial to reducing work-related stress among nurses.
Keywords: determinants; nurses; work related stress.
© 2022 Tsegaw et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Time management practice and associated factors among health professionals working in public and private hospitals in Dessie City, Northeast Ethiopia: a comparative cross-sectional study.Front Psychol. 2024 May 1;15:1366457. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1366457. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38751768 Free PMC article.
-
Burnout and associated factors among nurses working in public hospitals of Harari region and Dire Dawa administration, eastern Ethiopia. A cross sectional study.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 29;16(10):e0258224. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258224. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34714836 Free PMC article.
-
Job Satisfaction and Associated Factors among Health Professionals Working at Public and Private Hospitals in Bahir Dar City, Northwest Ethiopia: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Aug 26;2021:6632585. doi: 10.1155/2021/6632585. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34493980 Free PMC article.
-
Occupational stress and associated factors among nurses working at public hospitals of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2022; A hospital based cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2023 Apr 18;11:1147086. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1147086. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37143975 Free PMC article.
-
Work experience was associated with the knowledge and practice of catheter-associated urinary tract infection prevention among nurses at University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, northwest Ethiopia, 2021.BMC Womens Health. 2023 Jan 30;23(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02176-8. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 36717910 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Occupational stress and associated sources and risk factors among nurses in Gaza strip, Palestine: A cross-sectional survey.Nurs Open. 2024 Aug;11(8):e70004. doi: 10.1002/nop2.70004. Nurs Open. 2024. PMID: 39166300 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying the magnitude of stress among new graduate nurses working in intensive care units.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21078. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05253-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593997 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of work-related stress on patient safety culture among nurses in a tertiary hospital: a cross-sectional study.BMC Nurs. 2024 Jan 31;23(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01695-x. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38291420 Free PMC article.
-
Psychosocial Problems among Psychiatric Nurses for Caring Patients with Mental Disorders during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Nurs Res Pract. 2023 Jun 24;2023:3689759. doi: 10.1155/2023/3689759. eCollection 2023. Nurs Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37441199 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming nursing work environments: the impact of organizational culture on work-related stress among nurses: a systematic review.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Dec 2;24(1):1526. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-12003-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39623348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdali Bardeh M, Naji S, Zarea K. The study of job stress and tension management among oncology nurses of Ahvaz Hospitals in 2015. Int J Med Res Health Sci. 2016;5:189–199.
-
- Bruno L. Sources and effects of stress on work performance, and coping strategies among nurses at University of Cape Coast Hospital, Cape Coast, Ghana. J Chem Inf Model. 2019;53(9):1689–1699.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

